Highlights
May 10, 2024
Center for Dynamics and Control of Materials (2017)
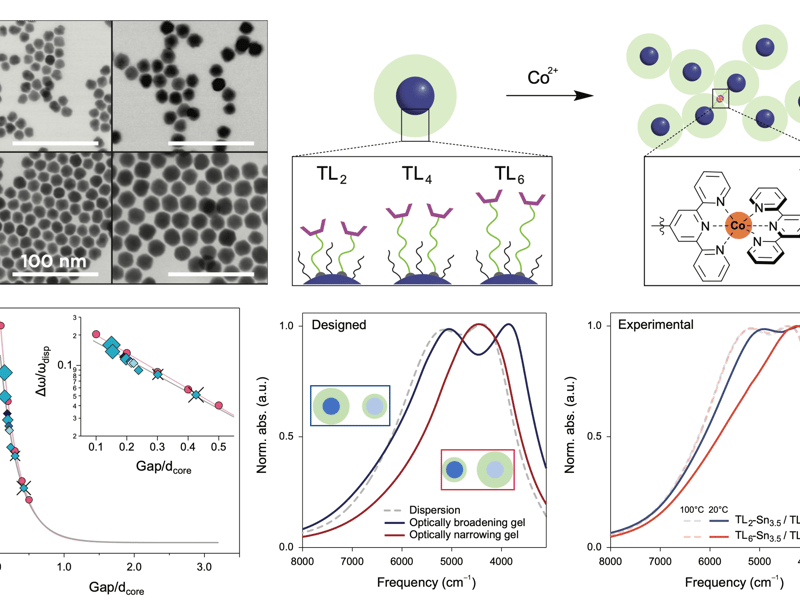
Structure tunable optical properties in linked nanocrystal gels
Optical properties of plasmonic ITO nanocrystal gels, assembled by thermoreversible cobalt terpyridine links, were tuned systematically based on the size and doping concentration of the nanocrystals and length of the custom ligand molecules. Correlation of optical shifts upon assembly with nanocrystal spacing deduced by small angle X-ray scattering was used to develop a universal structure-property relationship that was validated by large-scale optical simulations on gels made using Brownian dynamics simulations.
May 10, 2024
Center for Dynamics and Control of Materials (2017)
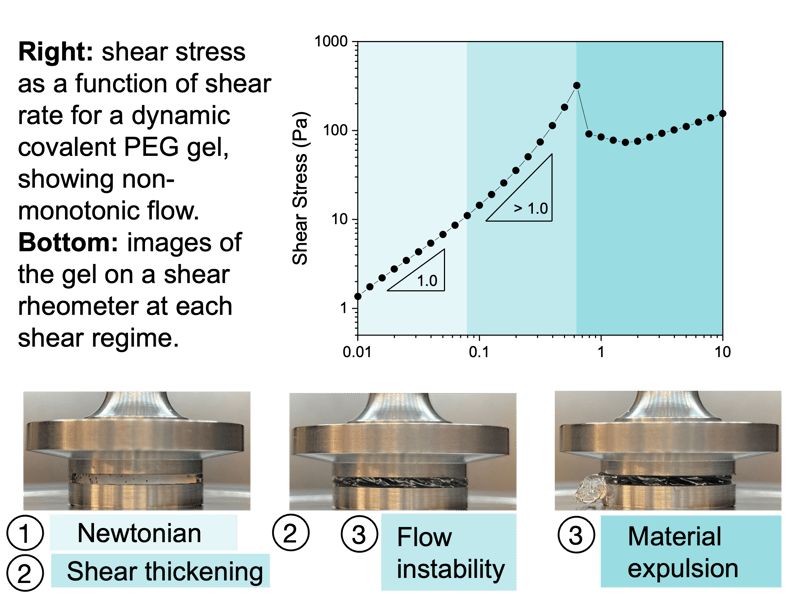
Nonlinear Rheological Behavior of Dynamic Covalent Gels
UT Austin researchers developed synthetic multi-arm poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG) hydrogels with three different dynamic covalent linking chemistries. They exhibit non-monotonic flow curves under steady shear, with shear thickening behavior that depends on the crosslinking bond exchange kinetics and polymer concentration.
May 10, 2024
Center for Dynamics and Control of Materials (2017)
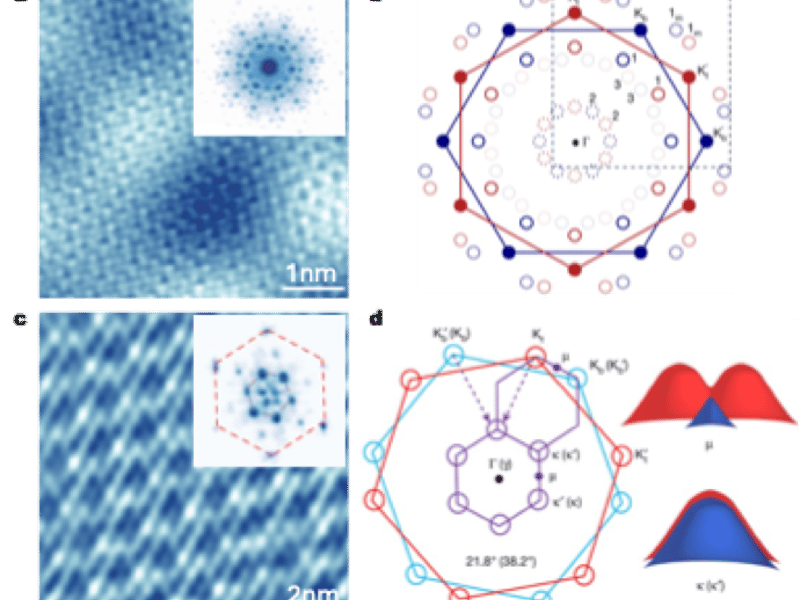
Tuning commensurability in twisted van Der Waals (vdW) bilayers
This study by UT Austin researchers demonstrates the rich electronic structures in large-angle twisted bilayer WSe2 exemplified by the formation of multiple mini-gaps near the valence band maximum. By tuning the commensurability, the moiré material properties and functionalities can be precisely engineered.
May 10, 2024
Center for Dynamics and Control of Materials (2017)
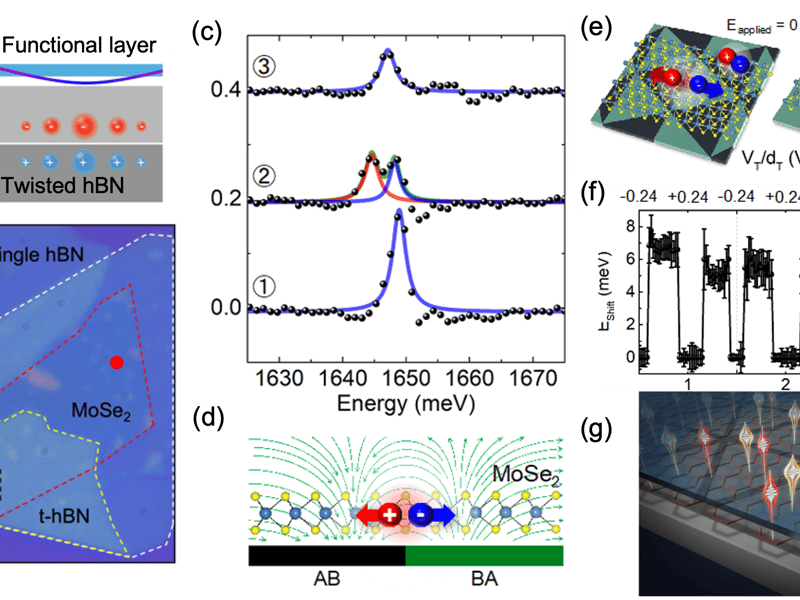
Harnessing moiré ferroelectricity to modulate light emission from a semiconductor monolayer
UT Austin MRSEC researchers show that ferroelectric polar domains formed in a twisted hexagonal boron nitride (t-hBN) substrate can modulate light emission from an adjacent semiconductor monolayer. The abrupt change in electrostatic potential across the domains produces an in-plane electric field (E-field) and leads to a remarkably large exciton Stark shift in the adjacent MoSe2 monolayer, previously only observable in p-n junctions created by the advanced e-beam lithography tools. Both the spectrum and spatial pattern of the light emission of the monolayer are periodically modulated by the remote moire potential imposed by the t-hBN substrate.

May 10, 2024
Center for Dynamics and Control of Materials (2017)
The Materials Universe Podcast: Bringing Materials Research to the General Public
CDCM has designed and launched one of the few materials science podcasts available to the public. The first season will feature 6 episodes where the podcast host, Abbey Stanzione, interviews CDCM MRSEC faculty about their educational backgrounds, pathway into academia and their cutting edge materials science research.
May 10, 2024
Illinois Materials Research Science and Engineering Center
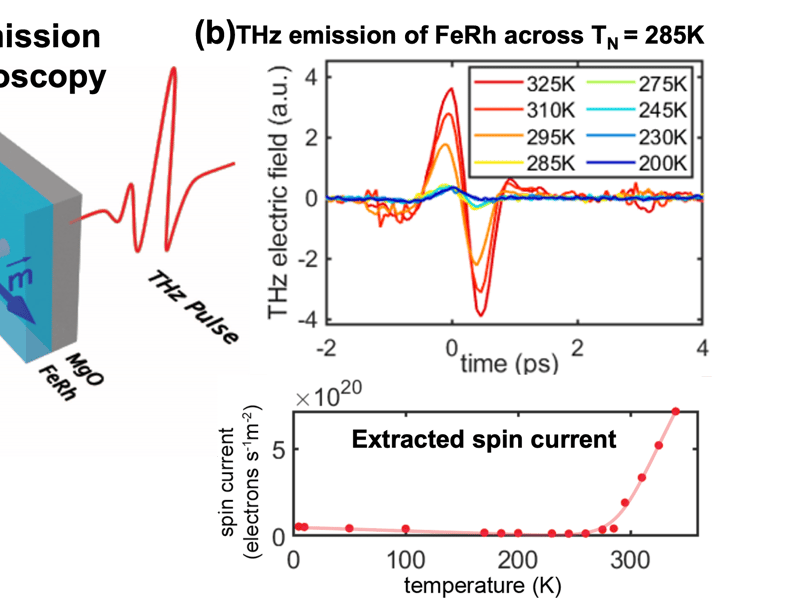
Ultrafast THz emission spectroscopy of spin currents in the metamagnet FeRh
THz emission spectroscopy developed at UIUC is used to investigate spin current generation in the antiferromagnetic metal FeRh under ultrafast laser excitation. The transient spin current in FeRh can be extracted from the emitted THz field. Developing viable platforms for the transduction between charge and spin current is crucial for spintronic based electronic devices. The Illinois MRSEC's work investigates FeRh as one such platform.

May 10, 2024
Illinois Materials Research Science and Engineering Center
Speaker Kits to Engage Middle Schoolers in Magnetism Science
In February 2024, I-MRSEC investigator Daniel Shoemaker, grad student Emily Waite, and outreach coordinator Pamela Pena Martin taught 35 7th and 8th graders at Franklin STEAM Academy, a Champaign public middle school, about magnetism through a kit they developed, supported by the I-MRSEC and a grant from the APS Group on Magnetism and its Applications. This visit was part of an annual 7-week program that teaches materials science concepts through hands-on activities aimed to build interest and confidence in STEM.
May 6, 2024
Big Idea: Synthetic Materials Biology
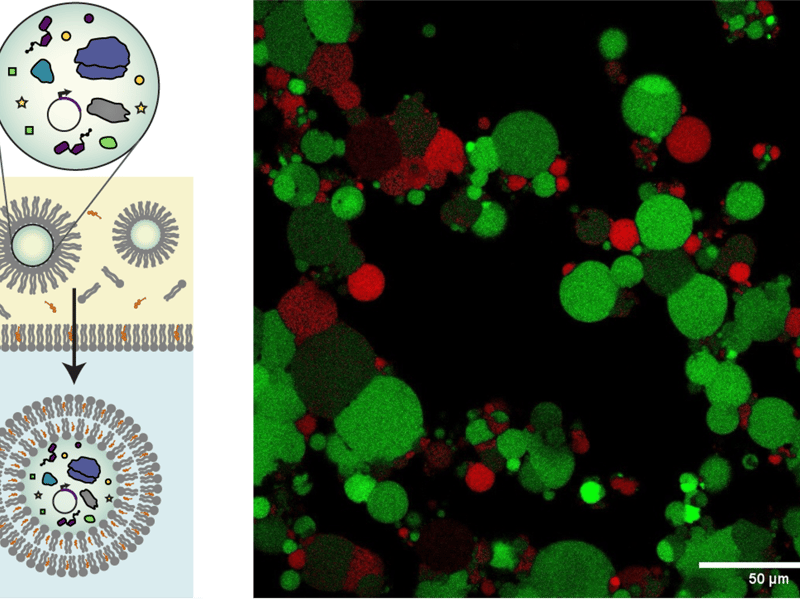
Encapsulating Cell-Free Reactions in Hydrogels
A critical element of Northwestern University MRSEC IRG-1 is interfacing cell-free systems with abiotic materials in a way that supports cell-free reaction efficiency and kinetics. In this work, the capacity of bilayer-based compartments (e.g., liposomes, polymersomes) is being assessed to support encapsulated cell-free reactions upon their inclusion in a larger hydrogel matrix.
May 6, 2024
Big Idea: Future of Work at the Human-Technology Frontier
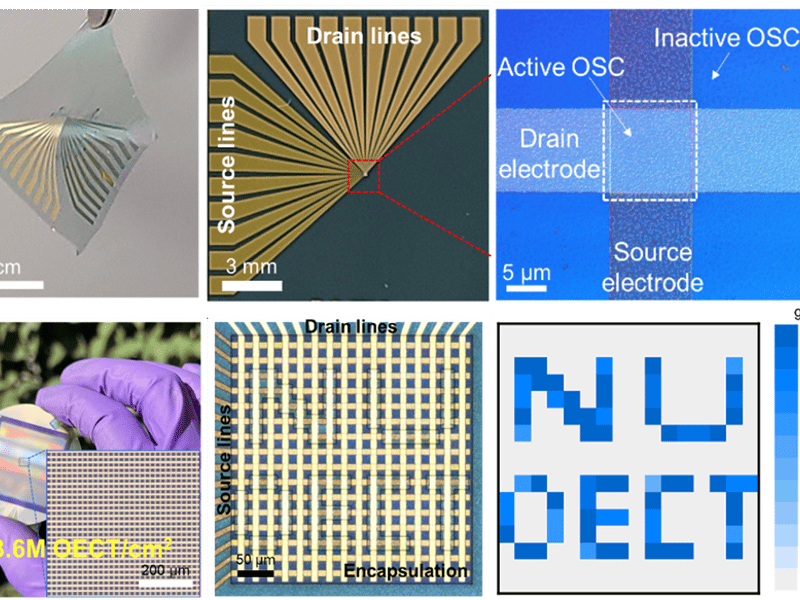
Monolithically Integrated Ultra-High-Resolution Vertical Organic Electrochemical Transistor Arrays and Complementary Circuits
Northwestern University MRSEC IRG-2 has realized ultra-high-density and mechanically flexible vertical organic electrochemical transistor (vOECT) arrays and complementary circuits through electron-beam patterning of the conjugated organic semiconductors by electron-beam exposure. The high energy electron-beam disrupts the conjugation in the exposed organic semiconductor area, creating an electronic insulator while retaining ionic conductivity and topological continuity with the redox-active unexposed areas.

Apr 1, 2024
Princeton Center for Complex Materials
Imaging and Analysis Center at Princeton University (2023-2024)
The Imaging and Analysis Center (IAC), supported by PCCM, is a world-leading facility for materials characterization. Its central mission is the education, research, and training of students at Princeton University and beyond. The IAC also collaborates with researchers in industry and other academic institutes.
Showing 91 to 100 of 1394