Highlights
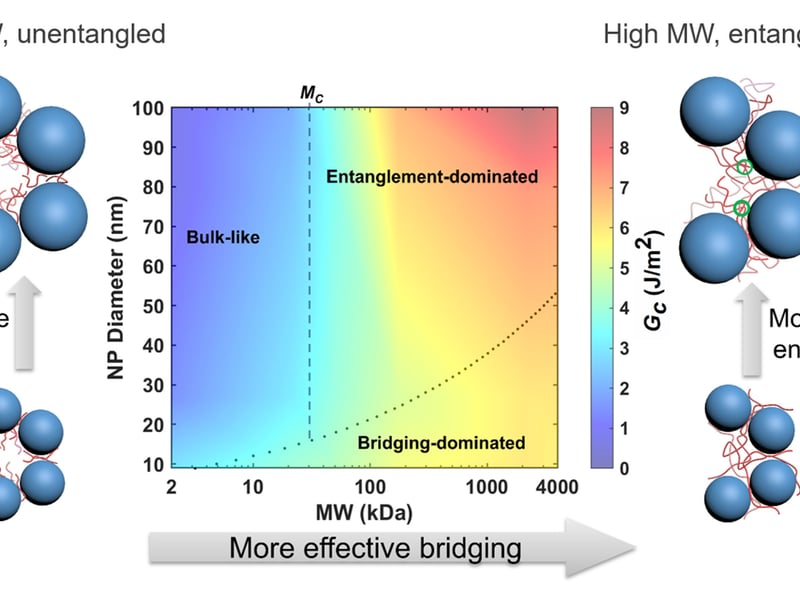
Toughening Infiltrated Nanoparticle Packings: Role of Bridging and Entanglement
Kevin Turner, Daeyeon Lee, University of Pennsylvania
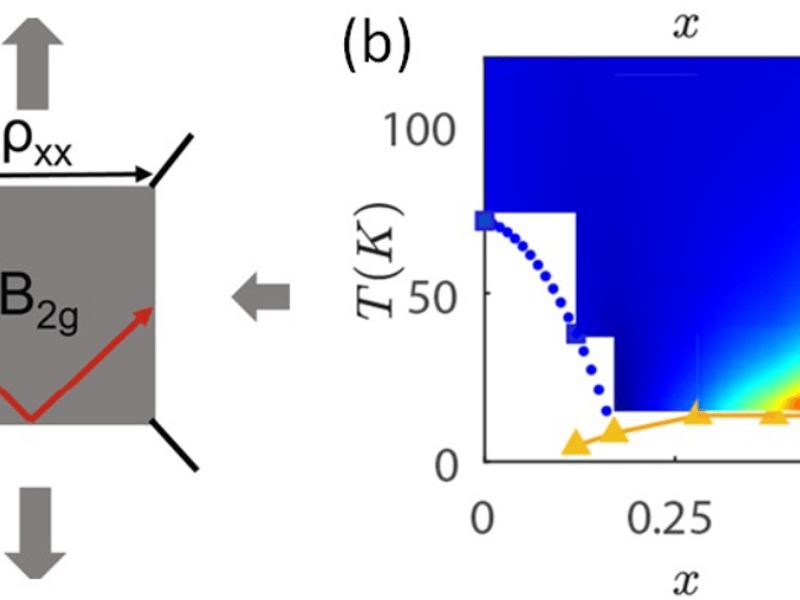
MEM-C IRG-2: Nematic Fluctuations in an Orbital Selective Superconductor Fe1+yTe1-xSex
Xiaodong Xu, Jiun-Haw Chu
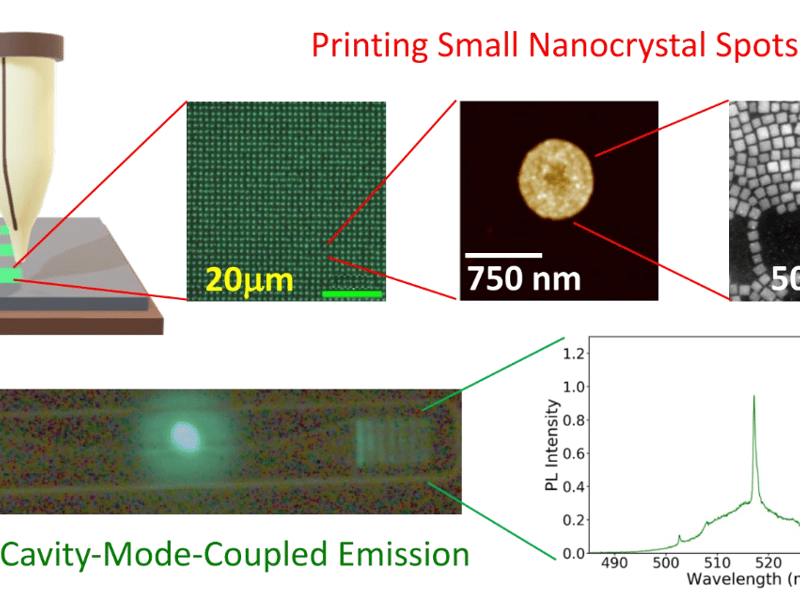
MEM-C IRG-1: Patterning Nanocrystals on Photonic Cavities with Electrohydrodynamic Inkjet Printing
Devin MacKenzie, Daniel Gamelin, Christine Luscombe, Jim De Yoreo, Arka Majumdar
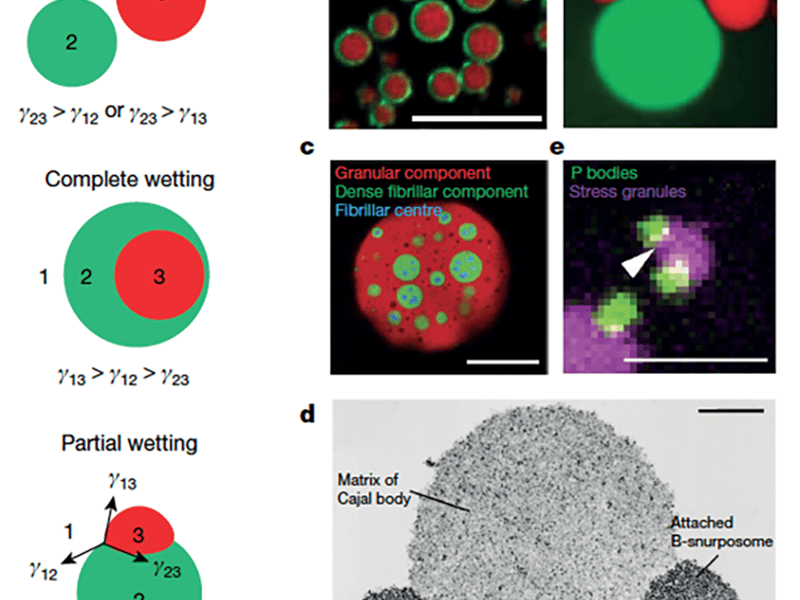
Capillary forces and biomolecular condensates: Structure and function
Bernardo Gouveia1, Yoonji Kim1, Joshua W. Shaevitz1, Sabine Petry1, Howard A. Stone1 and Clifford P. Brangwynne1 1 Princton University
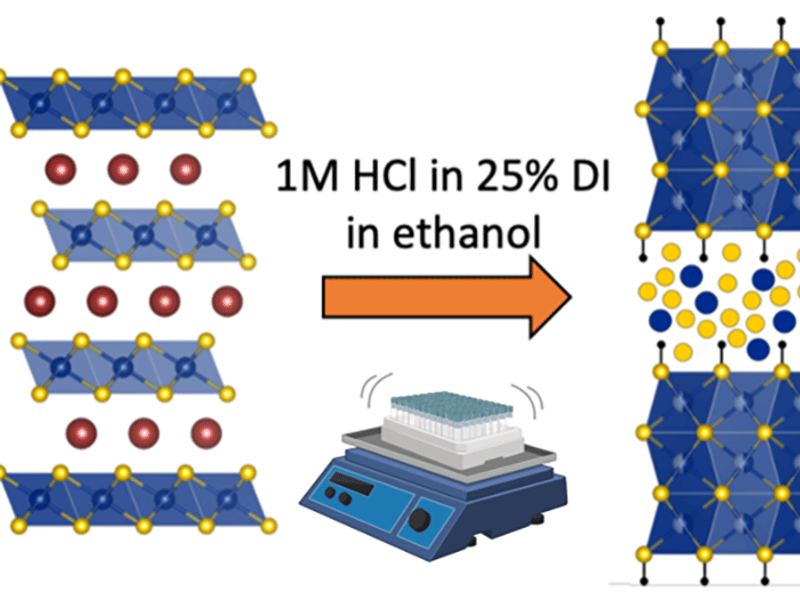
Unlocking High Capacity and Fast Na+ Diffusion of HxCrS2 by Proton-Exchange Pretreatment
J. W. Stiles1, A. L. Soltys1, X. Song1, S.H. Lapidus2, C.B. Arnold1, L. M. Schoop1 1 Princeton Univesity 2 Argonne National Laboratory
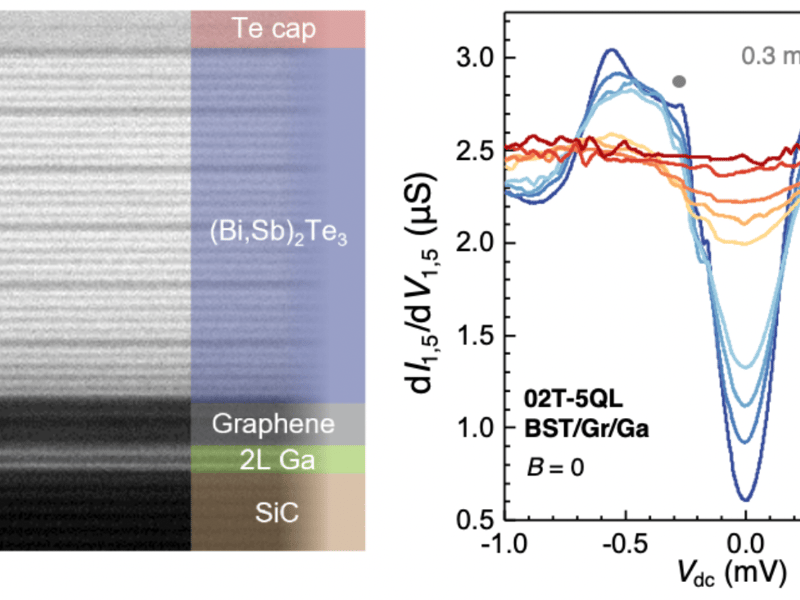
Proximity-induced superconductivity in epitaxial topological insulator/superconductor heterostructures
Zhu, Chang, Robinson, Hickey (PSU), Oreg (Weizmann Inst. of Sci.)
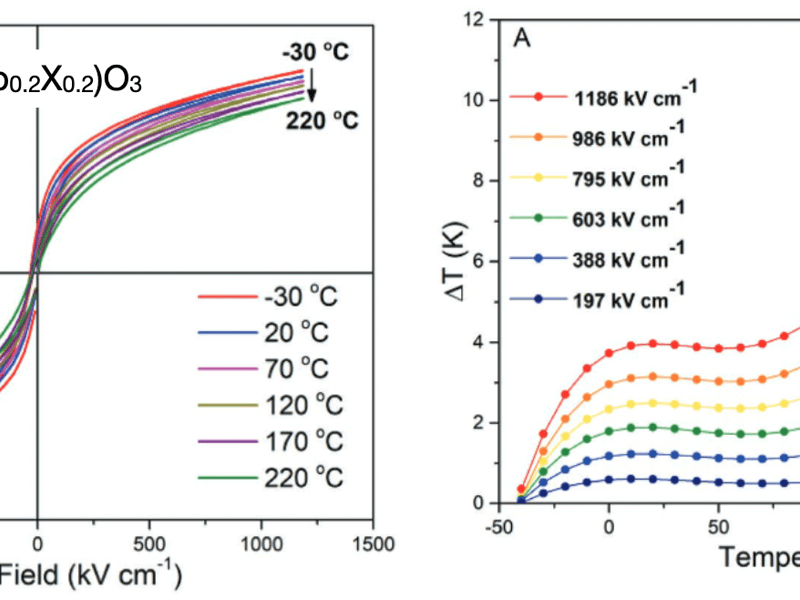
Electrocaloric Effect of Perovskite High Entropy Oxide Films
Y. Son and Susan E. Trolier-McKinstry, Penn State University
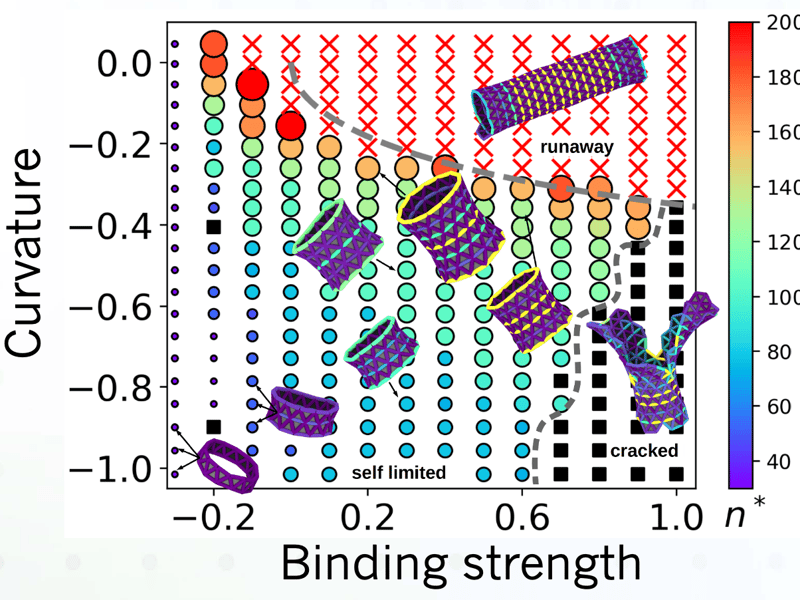
Frustrated self-limiting assembly of trumpets
Tyukodi, B.1, Mohajerani, F.1, Hall, D. M.2, Grason, G. M.2, and Hagan, M. F.1 1Brandeis University, 2U. Mass. Amherst
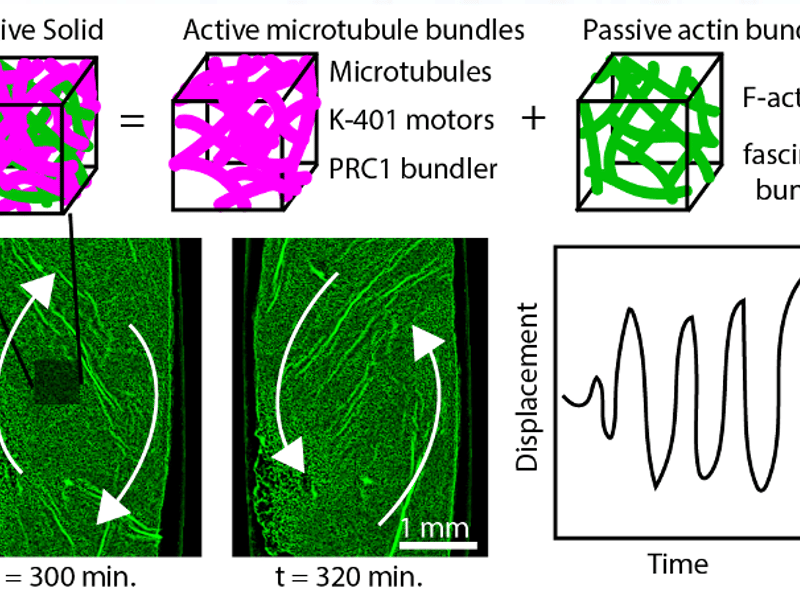
Active composite materials
1Fraden, 2Dogic , 1Baskaran, 1Chakraborty, 3Ramaswamy 1Brandeis University, 2UCSB, 3Indian Institute of Science
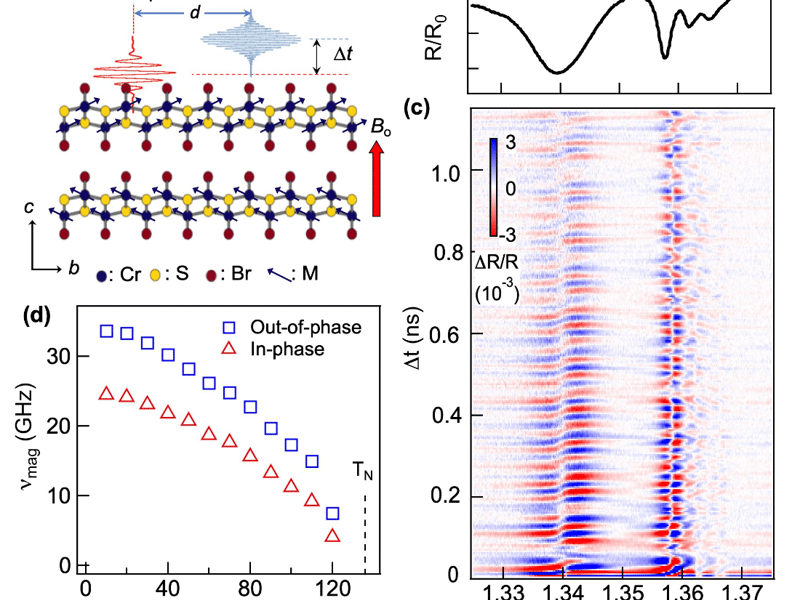
Exciton-Coupled Coherent Magnonsin a 2D Semiconductor
Zhu, Roy, Delor, Columbia University Center for Precision-Assembled Quantum Materials (PAQM)
Showing 121 to 130 of 1396