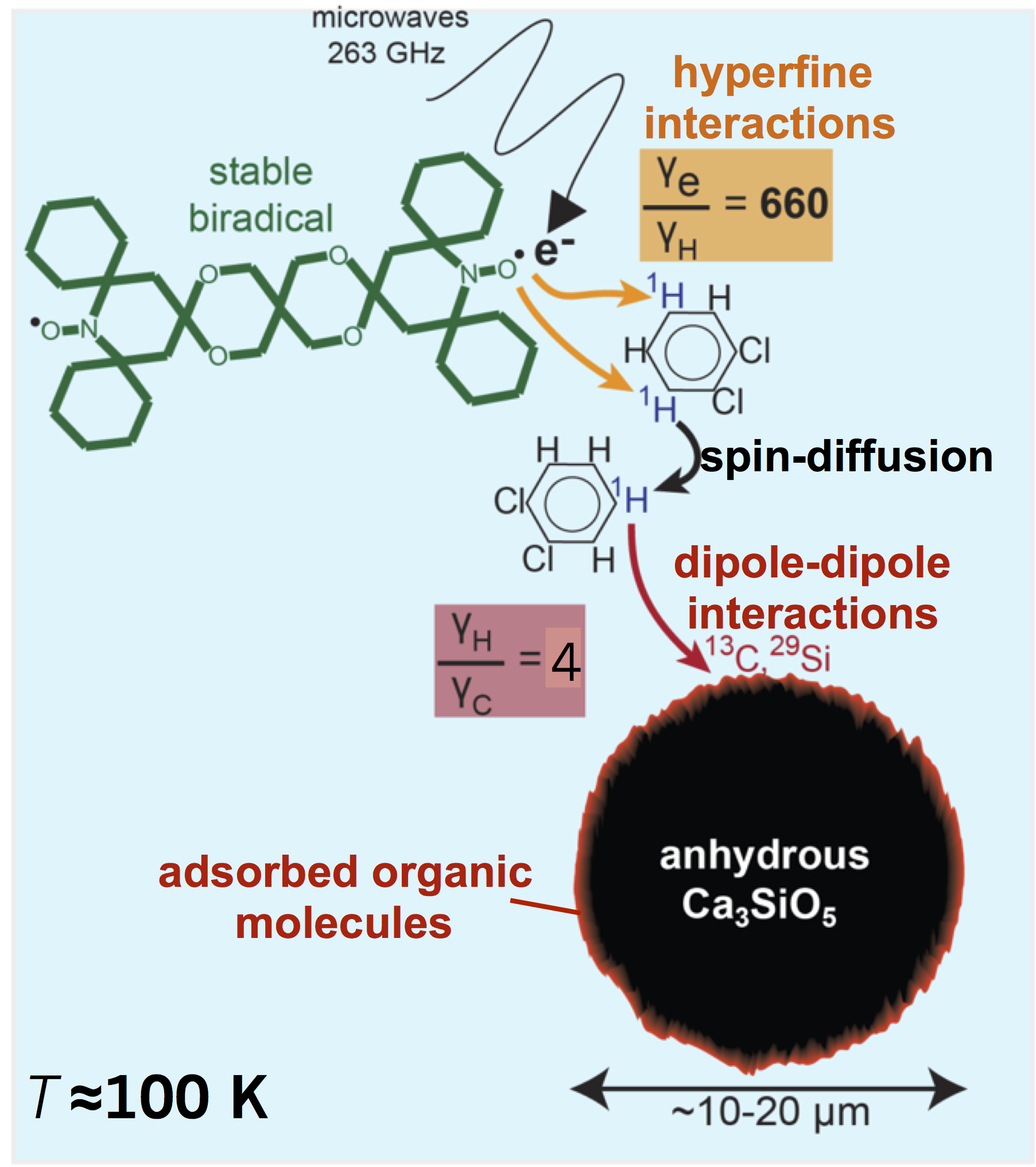
The DNP-NMR technique in the MRSEC Shared Experimental Facilities allows the selective measurement of surface species, in addition to enabling large sensitivity enhancements. The biradicals serve only to act as an antenna for the microwaves. Very small quantities of biradicals are introduced into the sample, which do not change the surface chemistry that results from hydration.

Materials Research Science and Engineering Center at UCSB
The NSF Materials Research Science and Engineering Center at UC Santa Barbara develops and sustains a productive, collaborative, and engaged community that drives a portfolio of transformative materials research and empowers a diverse workforce.