Highlights

Jun 14, 2017
CU Boulder Soft Materials Research Center (2014)
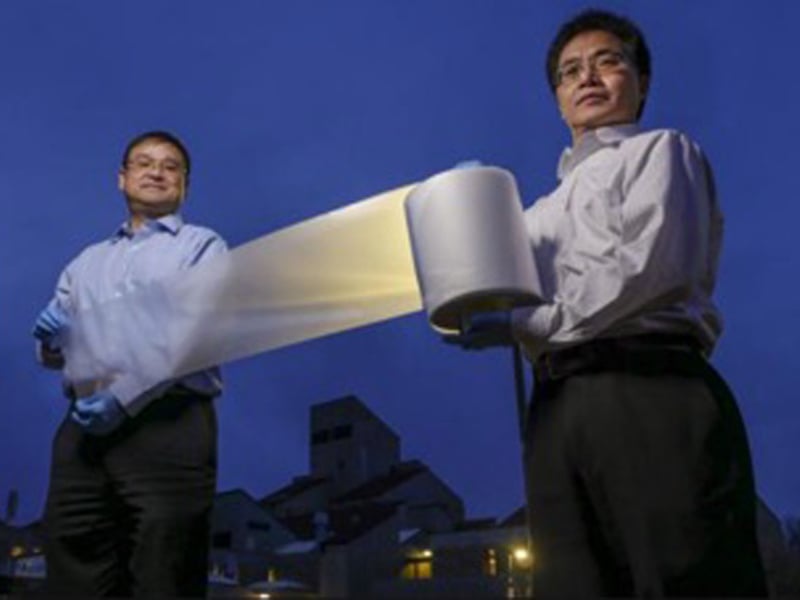
Inexpensive Polymer Films for Efficient Daytime Radiative Cooling
Xiaobo Yin & Ronggui Yang, University of Colorado Boulder
Researchers at the University of Colorado Boulder have made a discovery that explores an inexpensive way to eliminate waste heat in buildings, cooling systems, and even cars and trucks.

Jun 13, 2017
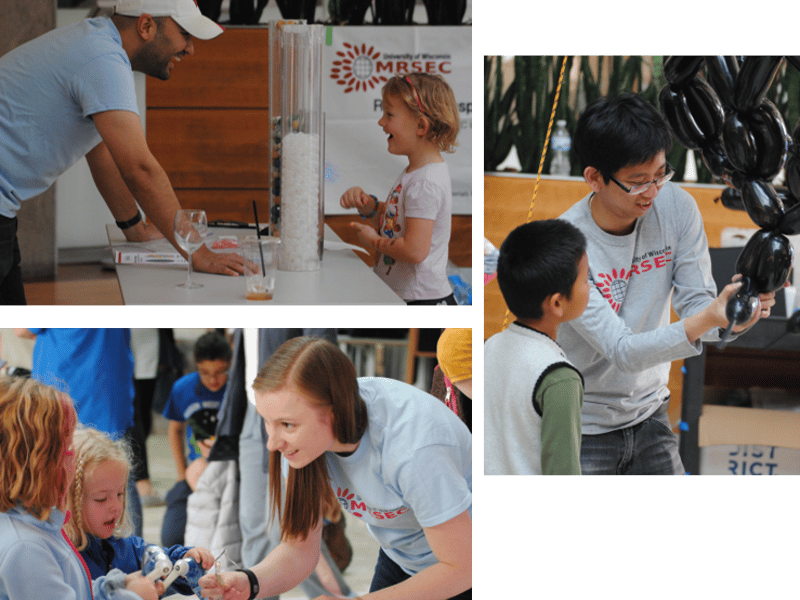
Wisconsin Materials Research Science and Engineering Center
MRSEC Members Teach the Public about Materials Science during the Wisconsin Science Festival
Anne Lynn Gillian-Daniel, University of Wisconsin-Madison
Over the course of two days, the Wisconsin MRSEC presented exciting hands-on, research-inspired materials science activities to over 1500 people during the 2016 Wisconsin Science Festival. The 2016 Wisconsin Science Festival was the largest ever with over 250 events in 20 communities across Wisconsin.
Jun 13, 2017
Wisconsin Materials Research Science and Engineering Center
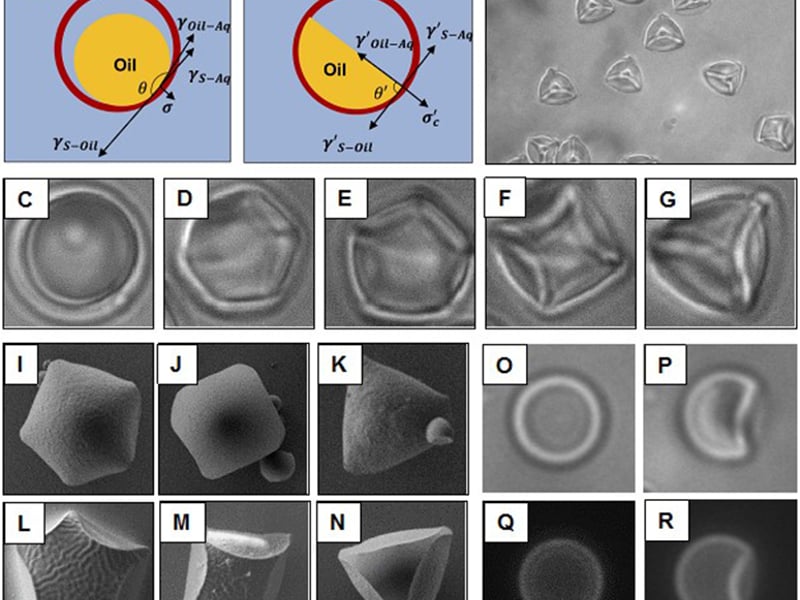
Synthesis of Non-Spherical Particles using Partially-Filled Polymeric Shells
N. L. Abbott, D. M. Lynn; University of Wisconsin-Madison
Spherical particles are easy to synthesize because a sphere is a shape that minimizes surface area. Non-spherical particles, however, have properties that can be very different from spherical particles, but they are challenging to fabricate.
Jun 13, 2017
Northwestern Materials Research Science and Engineering Center
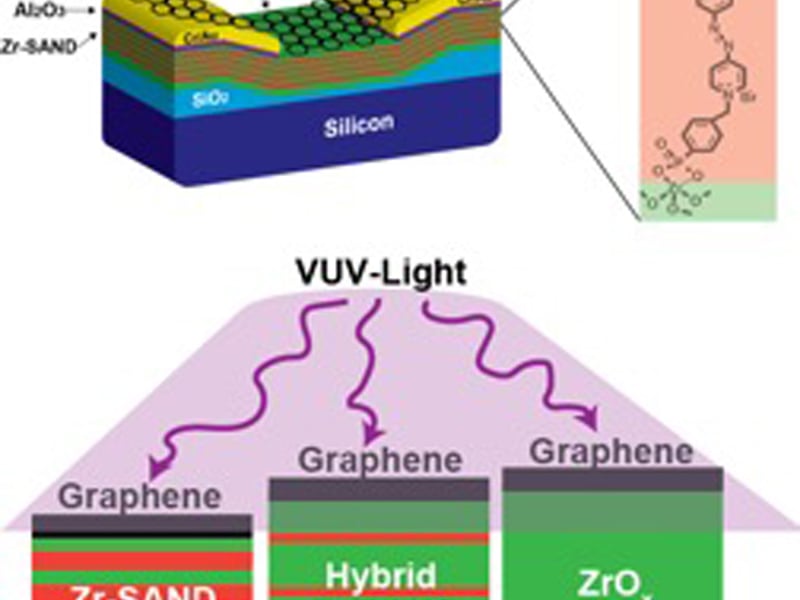
Radiation-Hard Graphene Electronic Devices via Hybrid Dielectrics
Mark Hersam and Tobin Marks, Northwestern University MRSEC
Solution-processed semiconductor and dielectric materials are attractive for satellite technology due to their light-weight, low-voltage operation, and mechanical robustness, but their response to ionizing radiation environments is not well understood.
Jun 13, 2017
Northwestern Materials Research Science and Engineering Center
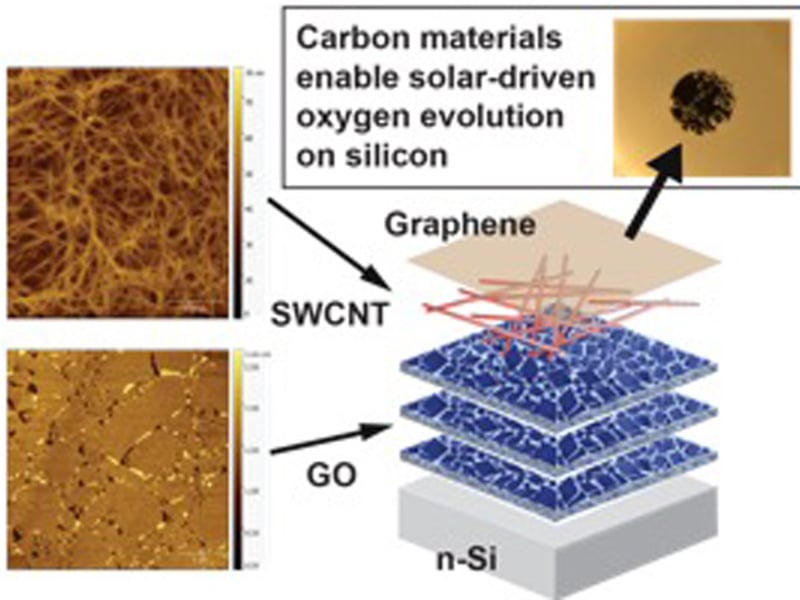
Metal-Free Carbon-Based Nanomaterial Coatings Protect Silicon Photoanodes in Solar Water-Splitting
Solar water splitting converts solar energy into chemical fuels that can be easily stored and transported. Silicon is already used on a large scale for photovoltaics, but it is unstable in the electrolytes used for water oxidation.
Jun 13, 2017
Northwestern Materials Research Science and Engineering Center
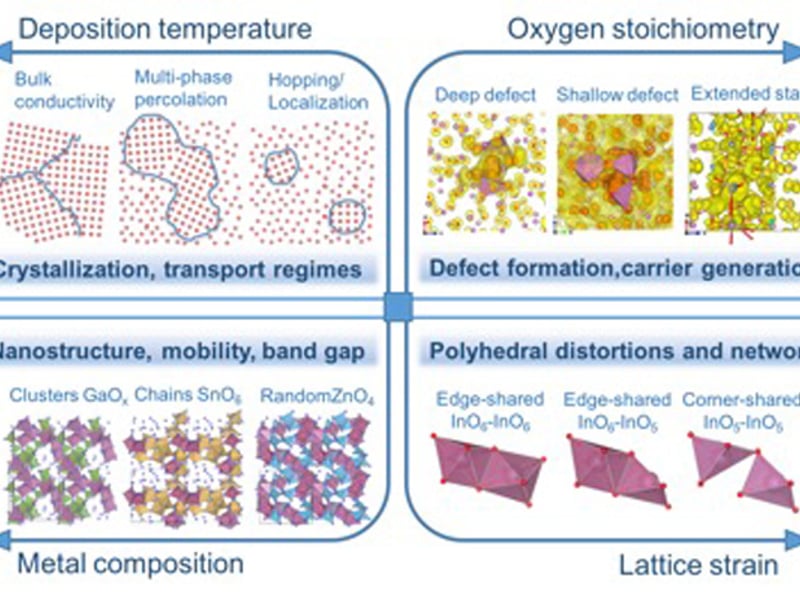
Parameter Space for Amorphous Oxide Semiconductors (AOSs)
Julia Medvedeva and Robert Chang, Northwestern University MRSEC
The combined results of controlled synthesis, ab-initio molecular-dynamics liquid-quench simulations, thorough structure and property characterization, and accurate density-functional calculations helped identify four major components that govern the electrical, optical, thermal, and mechanical properties of prototype In-based AOSs: (i) deposition temperature; (ii) oxygen stoichiometry; (iii) cation composition; and (iv) lattice strain, Figure.
Jun 13, 2017
Northwestern Materials Research Science and Engineering Center
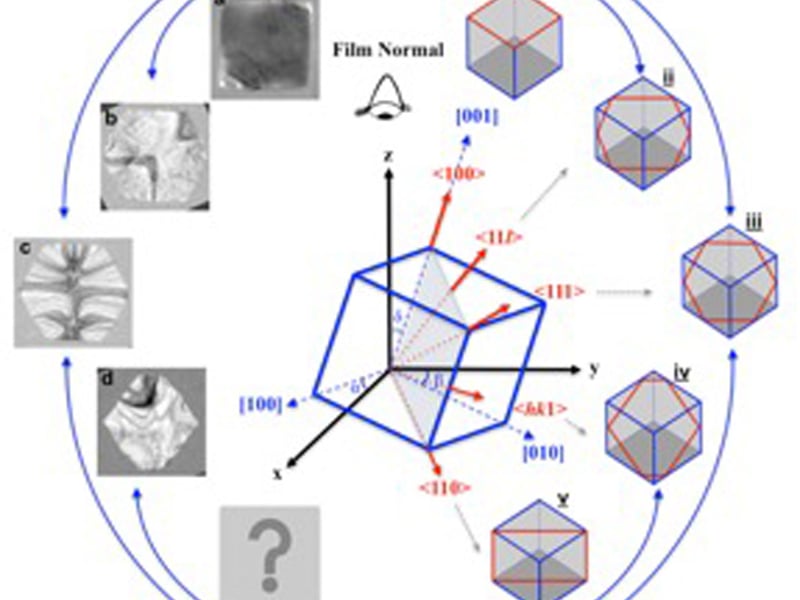
In-situ Crystallization and Morphological Evolution in Multicomponent Indium Oxide Thin Films
Peter Voorhees and Vinayak Dravid, Northwestern University MRSEC
Among all Transparent conducting oxides, Zinc-Indium-Tin Oxides are known for their good chemical stability, smooth surfaces and most importantly, high electrical conductivity. Having access to fundamental information like kinetics parameters is extremely important for processing and fabrication of these materials.
Jun 13, 2017
Northwestern Materials Research Science and Engineering Center
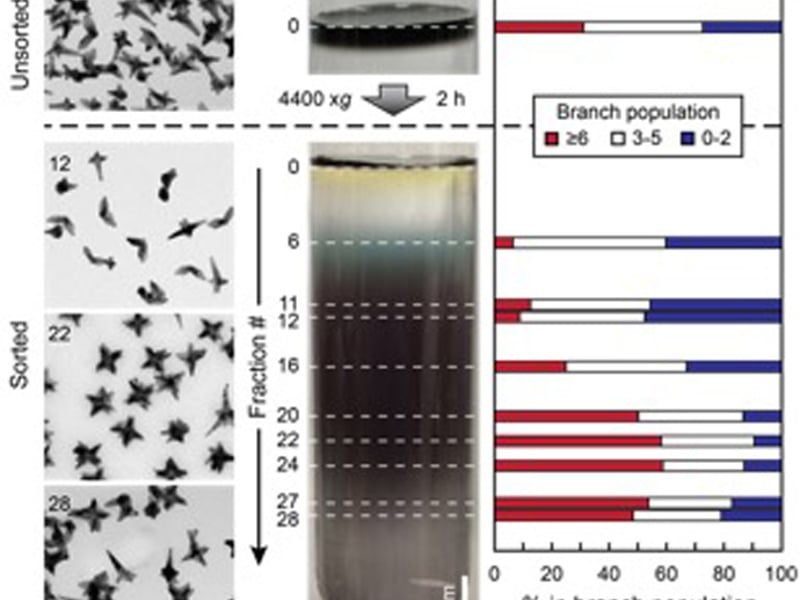
Homogeneous Gold Nanostars
Mark Hersam and Teri Odom, Northwestern University MRSEC
Anisotropic gold nanoparticles have been shown to possess desirable plasmonic and optical properties at the single particle level, but ensemble averaged measurements are compromised by the as-synthesized polydispersity in nanoparticle size and shape.
Jun 13, 2017
Northwestern Materials Research Science and Engineering Center
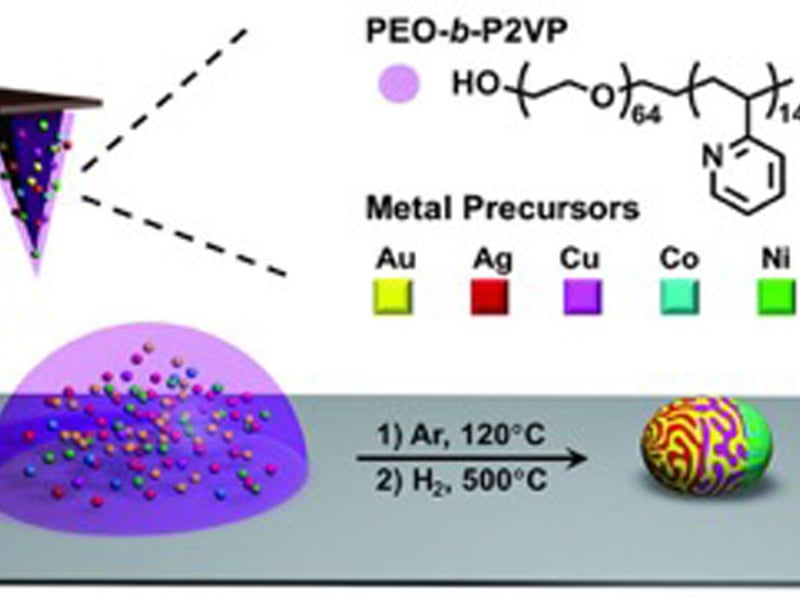
Polyelemental Nanoparticle Libraries
M. Hersam, V. Dravid, C. Mirkin, Northwestern University MRSEC
Multimetallic nanoparticles are useful in many fields, yet there are no effective strategies for synthesizing libraries of such structures with systematic compositional tunability.
Jun 13, 2017
Northwestern Materials Research Science and Engineering Center
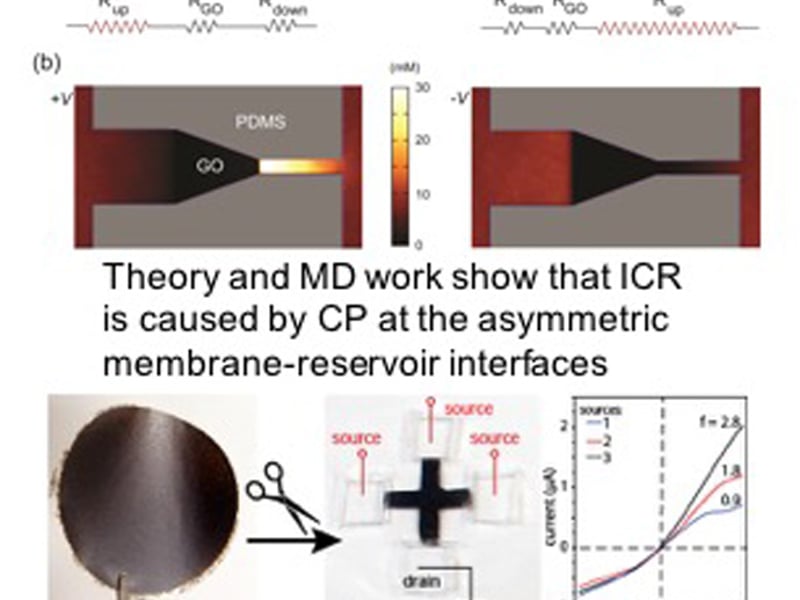
Kirigami Nanofluidics
J. Huang, E. Luijten, M. Olvera de la Cruz, Northwestern University MRSEC
Restacked films of exfoliated 2D nanosheets can function as massive nanofluidic channel arrays. Recent research shows that cutting such membranes into asymmetric shapes leads to ionic current rectification.
Showing 481 to 490 of 1394