Highlights
Jun 29, 2017
Columbia University in the City of New York
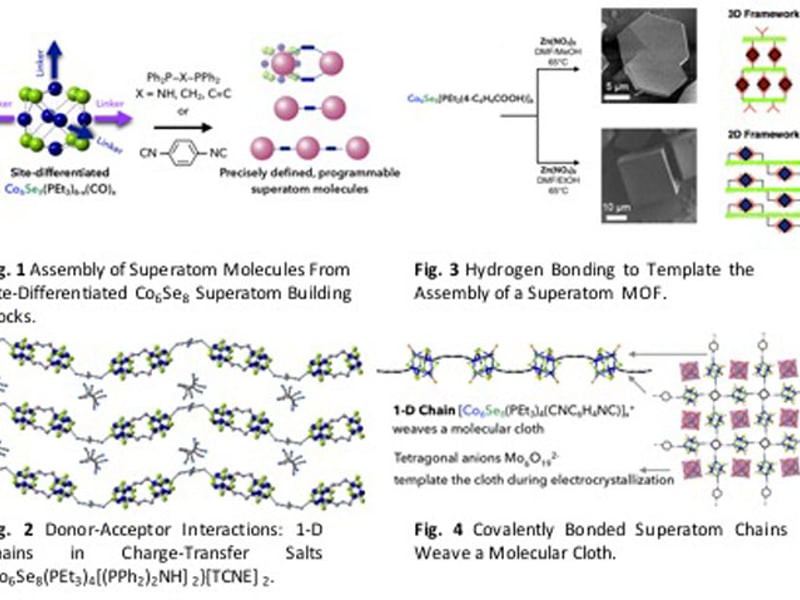
Programming Dimensionality in Superatomic Materials
Colin Nuckolls, Columbia University Center for Precision Assembly of Superstratic and Superatomic Solids
Featured as one of the “Ten Ideas That Will Change the World” in Scientific American in 2016, the discovery of assembling site-differentiated, atomically precise clusters into dimensionally controlled materials opens a new way to design and program a next generation of functional nanomaterials.
Jun 29, 2017
Columbia University in the City of New York
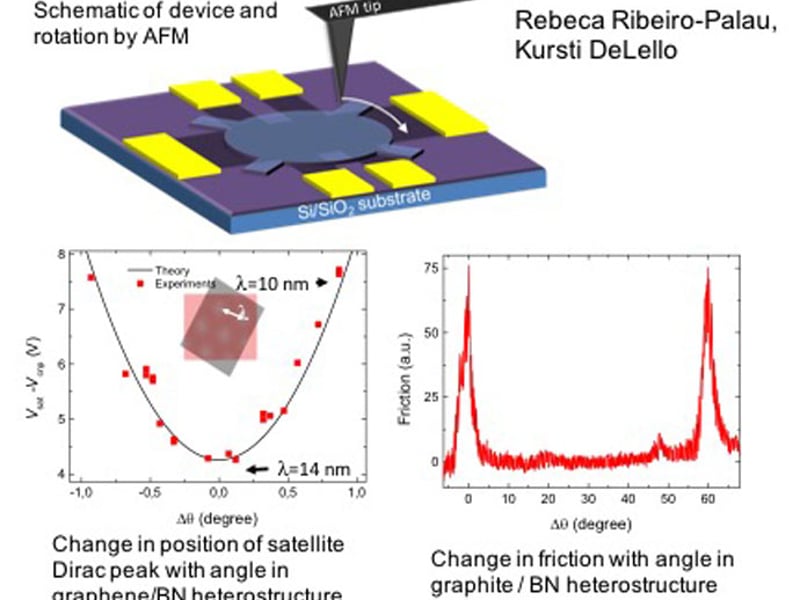
Rotating van der Waals Heterostructures
Cory Dean, Columbia University Center for Precision Assembly of Superstratic and Superatomic Solids
IRG1 of the Columbia MRSEC seeks to understand the behavior of van der Waals heterostructures created by assembly of atomically thin layered materials. One important question in this effort is how the relative orientation between the layers affects multiple properties.

Jun 27, 2017
Duke University
Efficient Generation of Long-lived Triplet Excitons in 2D Hybrid Perovskites
Stefan Zauscher, Director, Research Triangle MRSEC
Most recent work on hybrid organic-inorganic perovskites is focused on solar cell applications. Hybrid perovskites, however, provide a flexible platform for materials design, with prospects for many different applications.

Jun 27, 2017
Duke University
Magnetic Particle Chains for Directionally Controlled Actuation of Soft Robots
Stefan Zauscher, Director, Research Triangle MRSEC, Duke University
Researchers at North Carolina State University and Elon University have developed soft robots based on magnetic field-directed self-assembly of magnetic particles into chains embedded in elastomer films.

Jun 21, 2017
Brandeis University
Coherent Flows in Confined 3D Active Isotropic Fluids
Seth Fraden and Zvonimir Dogic, Brandeis University
Navier-Stokes equations dictate that the conventional fluid flows only in response to an externally imposed gradient in stress or a body force. We developed a novel active fluid that is comprised of microtubules and energy consuming molecular motors kinesin.
Jun 21, 2017
Brandeis University
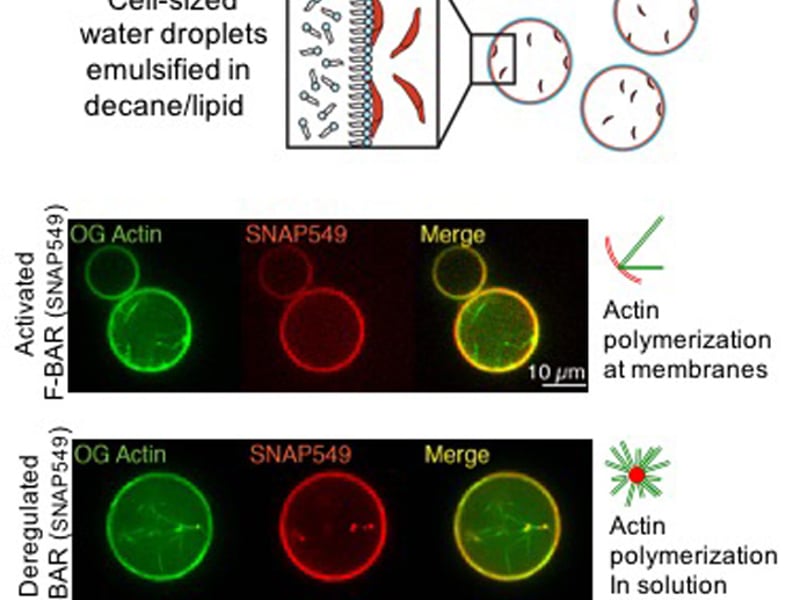
Directing Actin Polymerization to Membranes
C.F. Kelley, A.A. Rodal, Brandeis University
Biological membranes are deformed and shaped by proteins that assemble into higher-order scaffolds. These scaffolds target the force-generating polymerization of actin filaments to deform and shape the membrane.

Jun 16, 2017
Massachusetts Institute of Technology
RET Inspires Research Collaboration Between Middle School Students and MIT Research Group
The Research Experience for Teachers (RET) program at the MIT MRSEC immerses local science teachers in materials research on campus to increase their content knowledge, and develop pedagogical material for their classroom use.

Jun 16, 2017
Massachusetts Institute of Technology
Materials Deficient in Oxygen Show Promise in Magnetically Controlled Optical Devices
Profs. Harry Tuller and Caroline Ross
MIT MRSEC researchers, have created both polycrystalline and single-crystal films of iron-substituted metal oxides that show room temperature magnetism and magneto-optical properties depending on the oxygen pressure at which the films are grown and their resultant oxygen composition.

Jun 16, 2017
Massachusetts Institute of Technology
Using Light to Control the Viscoelastic Mechanical Properties of Gel-Like Materials
Profs. Bradley Olsen and Niels Holten-Andersen
MIT MRSEC researchers have developed stimuli-responsive hydrogel materials that can change their mechanical properties upon exposure to light. Insights generated from these studies will aid in the development of programmable hydrogels with specific stress-relaxing or energy-dissipating properties.

Jun 16, 2017
Massachusetts Institute of Technology
Tuning the Stability of Electronic Defects in Semiconducting Oxides
Profs. Caroline Ross and Krystyn Van Vliet
MIT MRSEC researchers have demonstrated that the combined action of temperature and mechanical stress can tune the relative stability of electronic defects in semiconducting oxides.
Showing 461 to 470 of 1396