Highlights
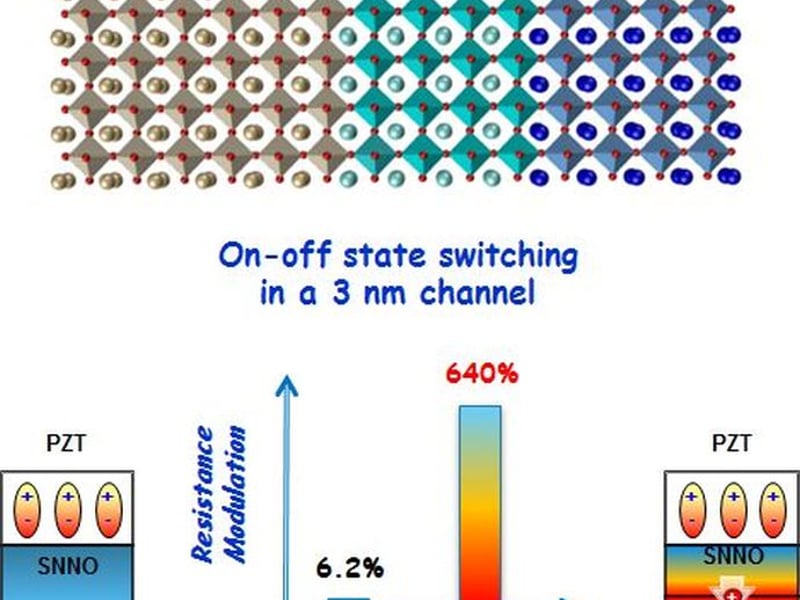
Interfacial Charge Engineering in Ferroelectric-Gated Mott Transistors
X. Chen, X. Zhang, M. A. Koten, Z. Xiao, L. Zhang, Jeffrey E. Shield, Peter A. Dowben and Xia Hong (University of Nebraska - Lincoln)

Building Enduring Pathways in STEM: Incorporating Traditional Ways of Knowing in Materials Research
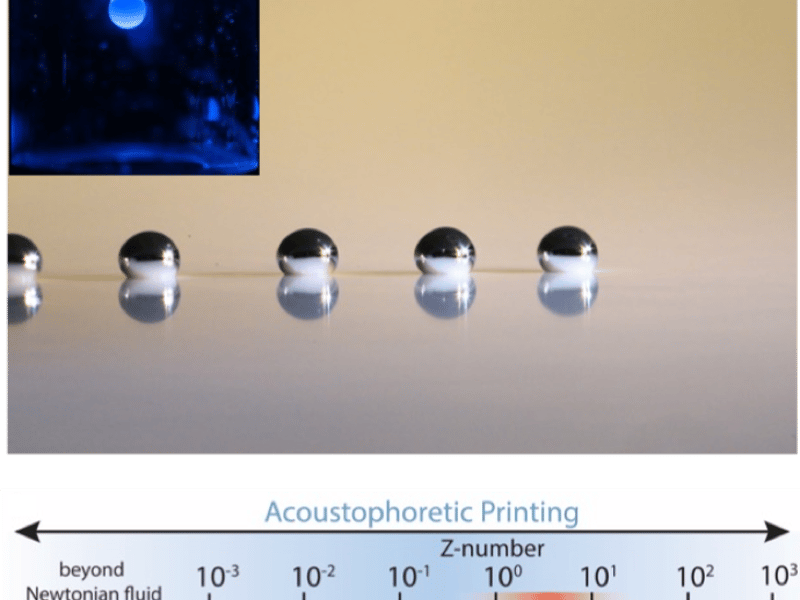
Acoustophoretic Printing: Printing Soft Materials with Sound
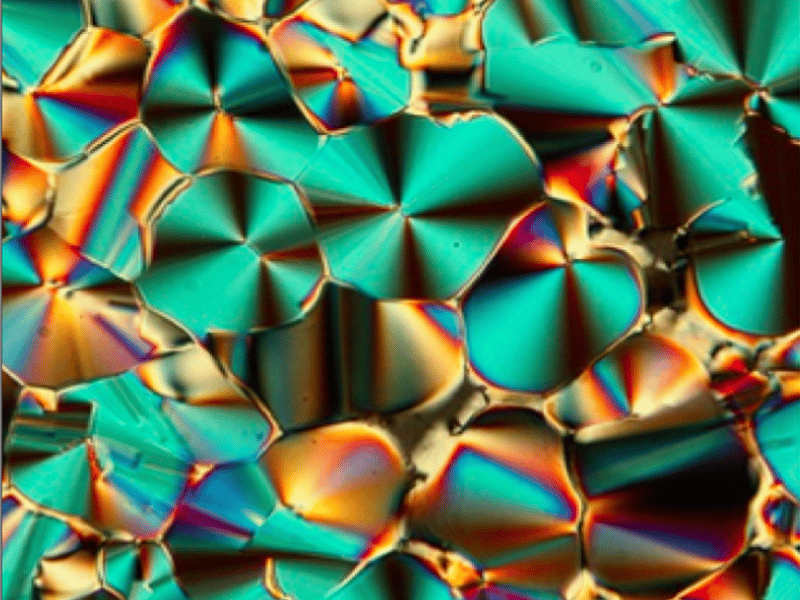
Microreactors for Abiotic Ligation of nanoRNA
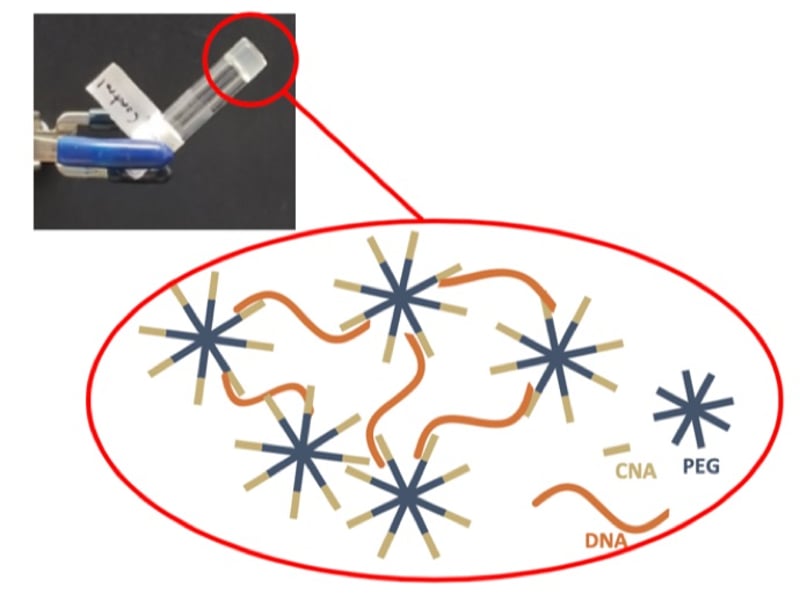
Hydrogels from DNA mimicking polymers and DNA
X. Han1, D.W. Domaille1, B.D. Fairbanks1, L. He1, H.R. Colver1, X. Zhang1, J.N. Cha1, C.N. Bowman1 1 Department of Chemical and Biological Engineering, University of Colorado, Boulder, CO 80309, USA.
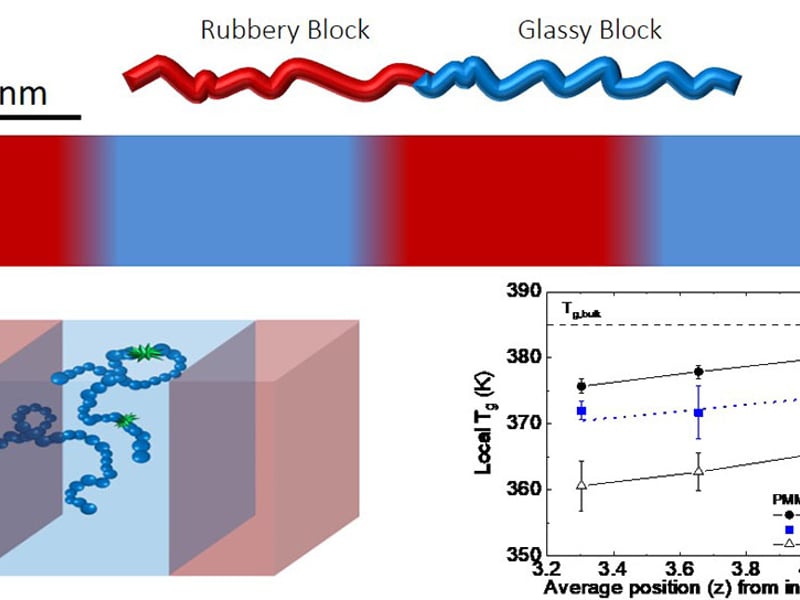
The Role of Chain Connectivity Across an Interface on the Dynamics of a Nanostructured Block Copolymer
D. Christie1, R.A. Register1, R.D. Priestley1, “The Role of Chain Connectivity Across an Interface on the Dynamics of a Nanostructured Block Copolymer,” Physical Review Letters, 121, 247801 (2018). 1Princeton University
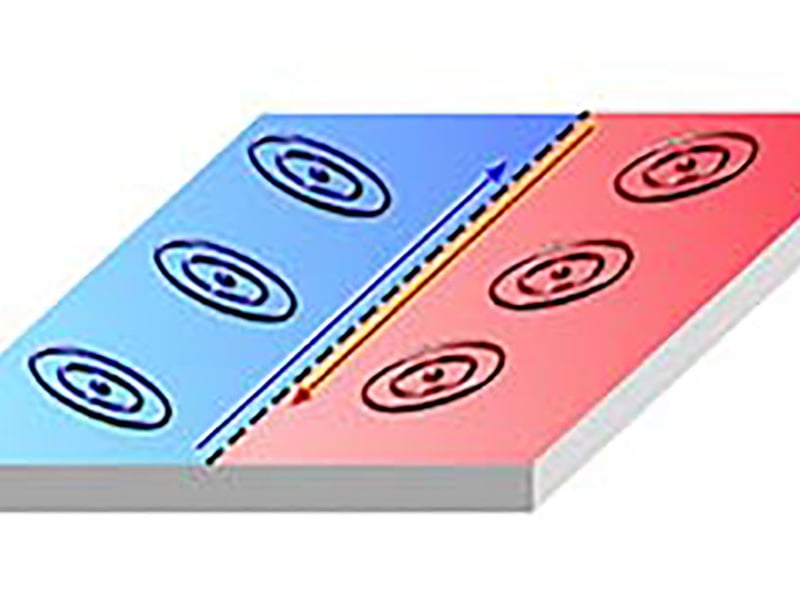
Controllable electron flow in quantum wires
M. T. Randeria1, K. Agarwal1, B. E. Feldman2, H. Ding1, H. Ji1, R. J. Cava1, S. L. Sondhi1, S. A. Parameswaran3 and A. Yazdani1 1 Princeton Univesity, 2 Stanford University 3 University of Oxford
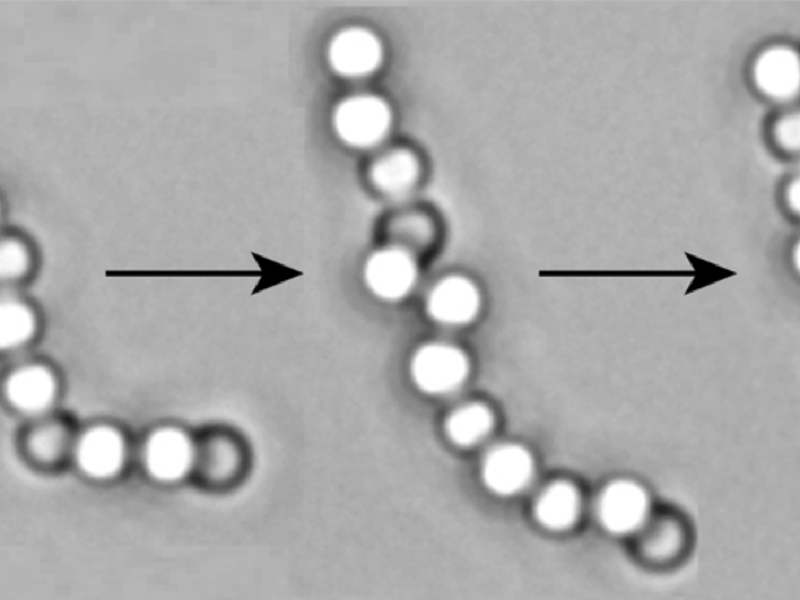
Freely Jointed Polymers Made of Droplets
Angus McMullen, Miranda Holmes-Cerfon, Francesco Sciortino, Alexander Y. Grosberg, and Jasna Brujic, New York University
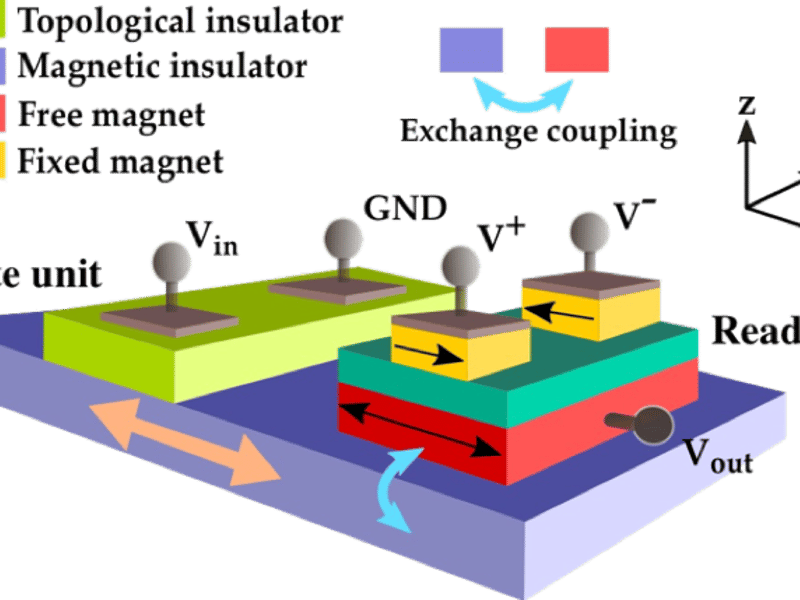
A Fully Voltage-Controlled Spin Logic Device
Rakheja, Flatté and Kent, New York University
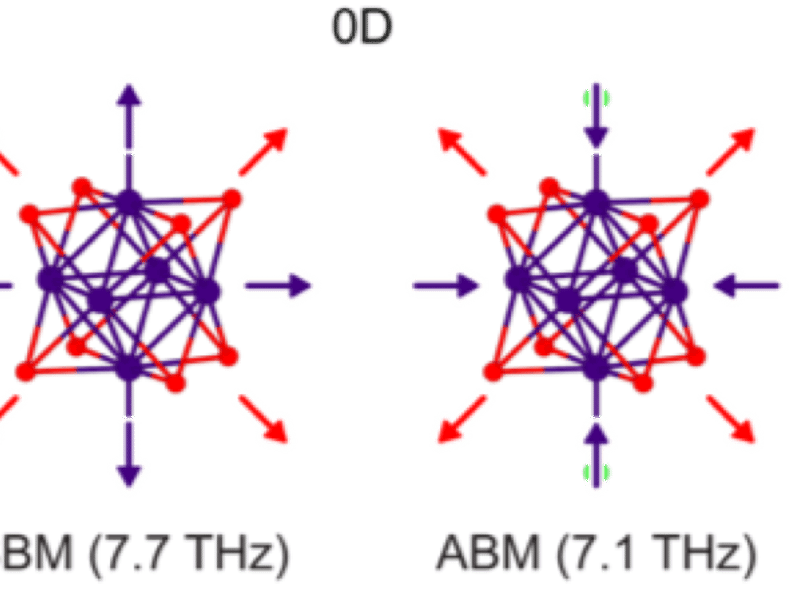
Hierarchical Coherent Phonons
Xiaoyang Zhu, Xavier Roy, Colin Nuckolls, Center for Precision Assembly of Superstratic and Superatomic Solids
Showing 311 to 320 of 1394