Highlights
Jan 27, 2014
Cornell University
Atomic Break Dancing in the World’s Thinnest Glass
P. Y. Huang, S. Kurasch, J. S. Alden, A. Shekhawat, A. A. Alemi, P. L. McEuen, J. P. Sethna, U. Kaiser, D. A. Muller, Science 342, 224-227 (2013)
Electron microscopy reveals the fundamental steps of bending
An international team of Cornell researchers and collaborators was recently entered into the Guinness Book of World Records for fabricating the world’s thinnest pane of glass — only two atoms thick!
Jan 22, 2014
University of Minnesota - Twin Cities
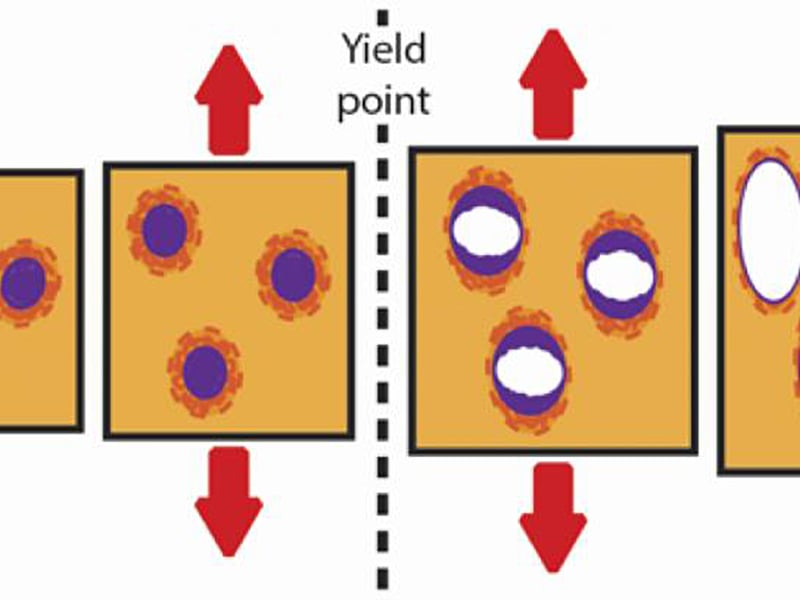
Cavitation in Block Copolymer Modified Epoxy Revealed by In Situ Small-Angle X-Ray Scattering
Frank Bates & Lorraine Francis (IRG-1)
Addition of rubber particles to epoxy thermosets has been successful for toughening these brittle materials.
Jan 22, 2014
University of Minnesota - Twin Cities
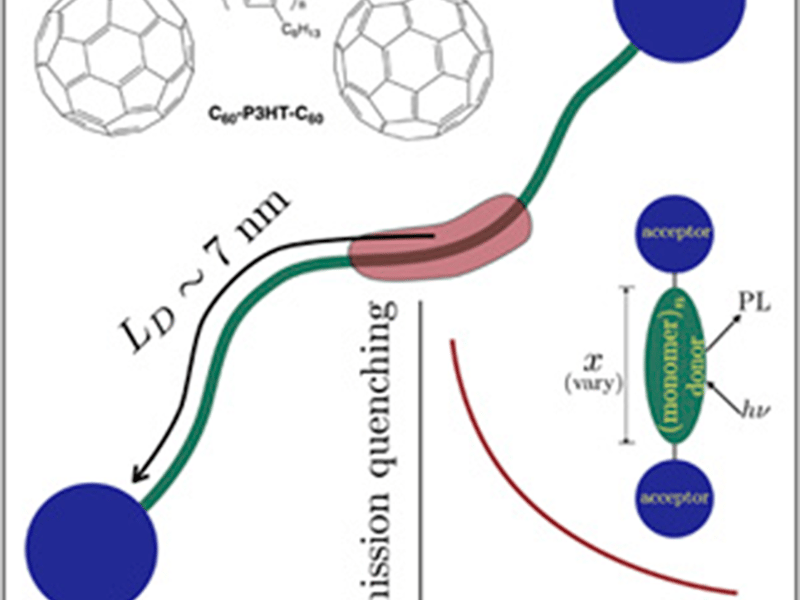
Intramolecular Exciton Transport in Conjugated Polymers
David Blank (IRG-2)
Using a series of acceptor-polymer-acceptor triads, IRG-2 investigators have measured intramolecular exciton diffusion in poly-3(hexylthiophene) (P3HT) for the first time.
Jan 22, 2014
University of Minnesota - Twin Cities
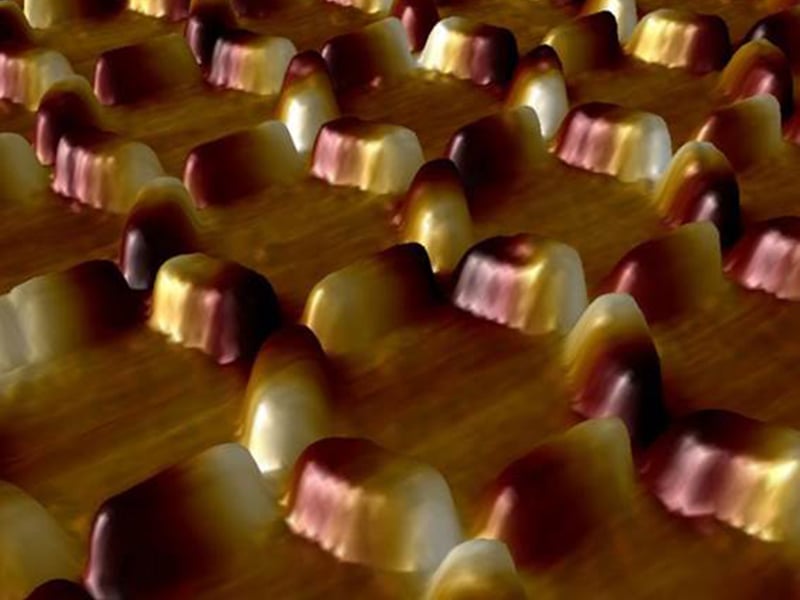
Magnetic Charge Crystallization in Artificial Spin Ice
Chris Leighton (IRG-3), in collaboration with the Univ. of Illinois, Penn State, and Los Alamos
“Artificial spin ice” is a term used for arrays of nanoscale magnetic islands on lattices that geometrically frustrate inter-island interactions.
Jan 22, 2014
University of Minnesota - Twin Cities
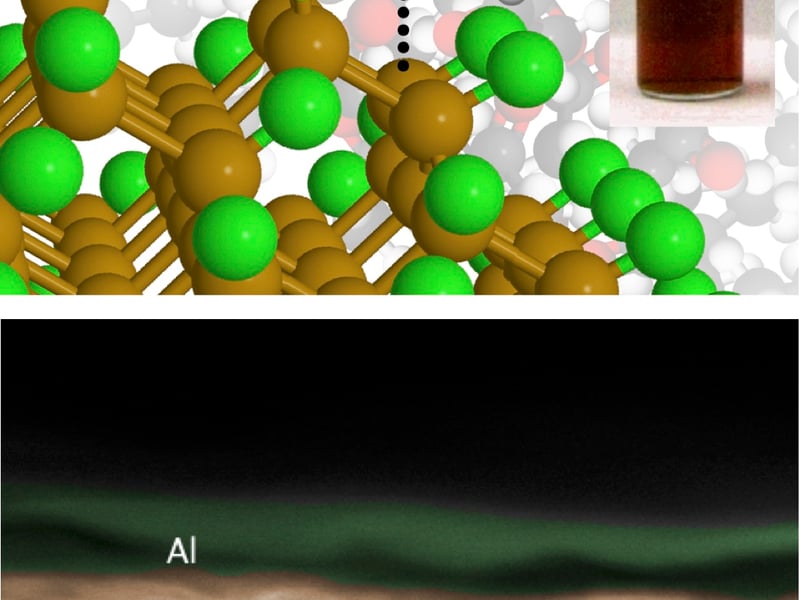
Ligand-free Colloids and Surface Doping of Silicon Nanocrystals
Uwe Kortshagen
Inks of inorganic nanocrystals hold great promise for printed electronics but the widely used organic surfactants (ligands) needed to stabilize these inks degrade the electrical quality of the printed films.
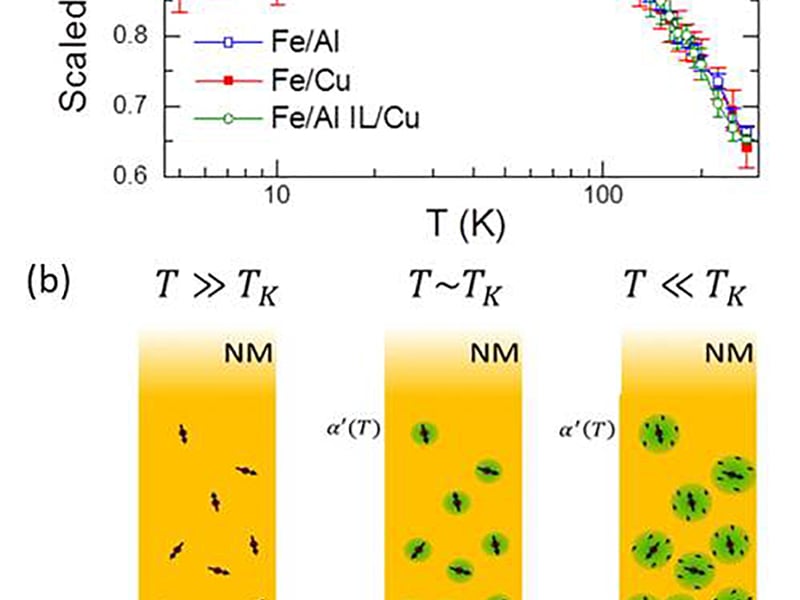
Jan 22, 2014
University of Minnesota - Twin Cities
Kondo Physics at Ferromagnet/Normal Metal Interfaces
P. A. Crowell and C. Leighton
The idealized picture of an interface between two elemental materials is simply an abrupt transition between planes containing two different types of atoms.
Jan 19, 2014
Northwestern University
Enhanced Refractive Index Sensing with Monodisperse Faceted Plasmonic Nanoparticles
Yu Jin Shin, Emilie Ringe, Michelle L. Personick, M. Fernanda Cardinal, Chad A. Mirkin, Laurence D. Marks, Richard P. Van Duyne, and Mark C. Hersam
The shape-dependent optical properties of metal
nanostructures have motivated efforts to correlate
nanoparticle structure with plasmonic behavior. In
particular, gold bipyramids (BPs) are of interest due
to their sharp tips that lead to strong localized field
enhancement and high sensitivity to the surrounding
environment. However, despite their potential,
relatively few reports have studied the optical
properties of sub-100 nm BPs due to their relatively
low synthetic yields. To overcome this issue, density
Jan 19, 2014
Northwestern University
Northwestern MRSEC Partnerships Nucleate New Centers
Northwestern MRSEC provides the physical and intellectual
infrastructure to nucleate collaborative opportunities in materials
research both on and off the Northwestern campus, and continues
to leverage its diverse portfolio of research into new educational
and commercial opportunities. Recent examples include:
Dec 5, 2013
University of Utah
Utah MRSEC Teaching the Teachers
Debra Mascaro, Utah MRSEC, University of Utah Mechanical Engineering.
Teaching the Teachers
Electromagnetism at the Physical Sciences Inquiry Academy
These fifth-grade teachers are building electromagnetic ping pong ball launchers to demonstrate electromagnetism to their students.
Utah MRSEC leads lessons and activities for teachers, as well as provides educational kits which supplement curriculum andcoordinate with Utah Core Standards.
Participants:
Showing 751 to 760 of 1396