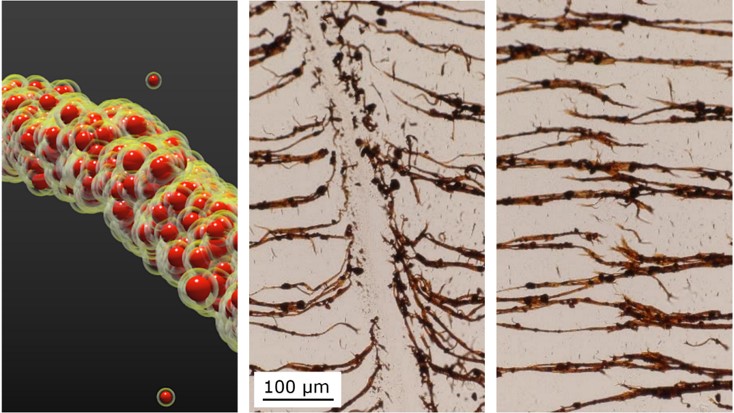
In a paper published in Nature Materials, researchers from North Carolina State University and the University of North Carolina-Chapel Hill show that magnetic nanoparticles encased in oily liquid shells can bind together in water, much like sand particles mixed with the right amount of water can form sandcastles.