 IRG1 has developed a toolkit for carrying out simulated X-ray adsorption spectroscopy (XAS). XAS is a powerful technique for understanding the surface local structure and chemistry of complex interfaces at the nanoscale.
IRG1 has developed a toolkit for carrying out simulated X-ray adsorption spectroscopy (XAS). XAS is a powerful technique for understanding the surface local structure and chemistry of complex interfaces at the nanoscale.
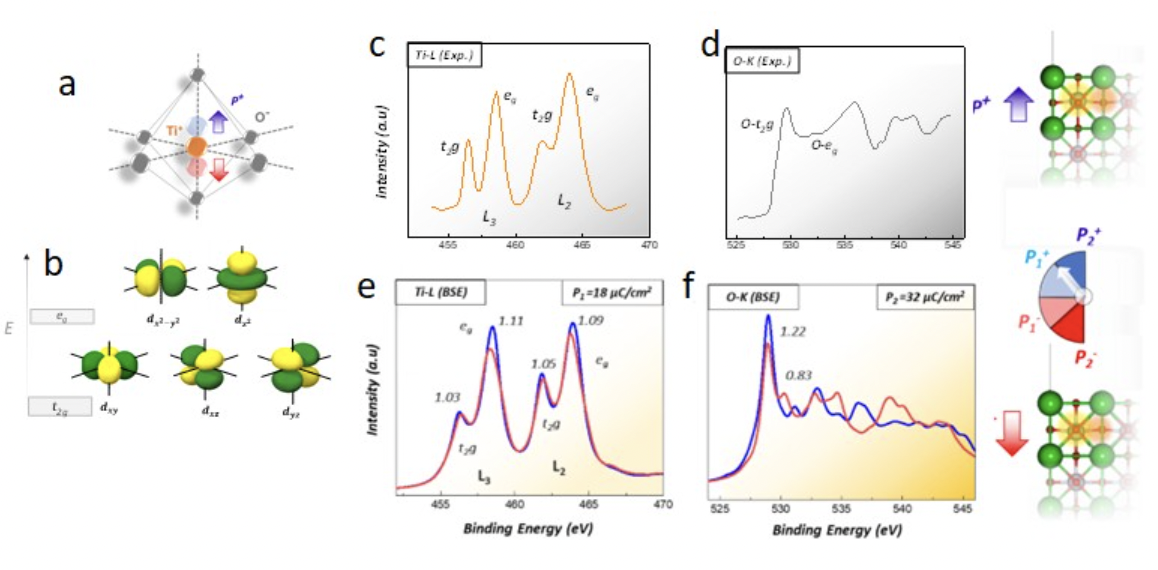
The team used XAS to understand the factors that contribute to changes in the electronic structure of ferroelectric BaTiO3 thin films from first-principles. The team was able to map out the energy landscape for this complex material, both computationally and spectroscopically.
This work expands the team’s knowledge of how materials operate at the atomic level, providing a rigorous accounting for materials physics and chemistry, such as polarization-induced surface reconstruction.