Highlights
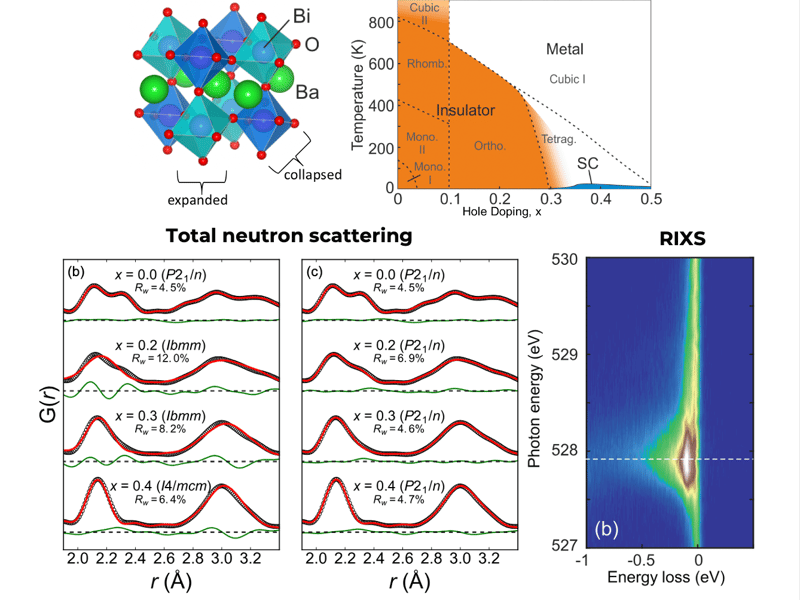
Persistence of Small Polarons in Doped Bismuthate Superconductors
University of Tennessee, Knoxville (UTK) Center for Advanced Materials and Manufacturing (CAMM)

Expanding CAMM’s Impact: REU Summer Outreach with Knoxville Youth
University of Tennessee, Knoxville (UTK) Center for Advanced Materials and Manufacturing (CAMM)
Experimenta Con PREM: Documenting Two Decades of Impact
Idalia Ramos, U. Puerto Rico, Humacao and Eric Stach, U. Pennsylvania

REU: New Emphasis on Science Communication
Mark Licurse & Ashley Wallace, University of Pennsylvania
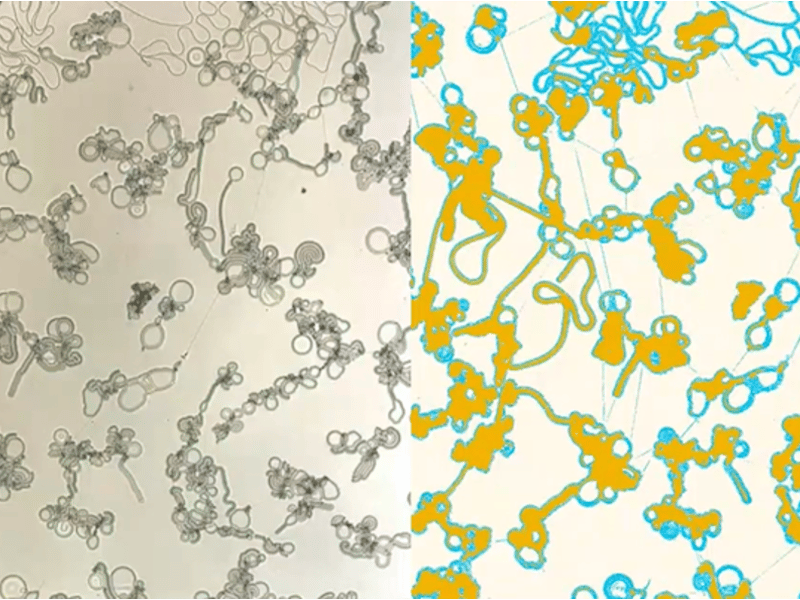
Self-Assembling Networks: A New Structured Fluid Architecture Through Phase Separation
Chinedum Osuji, University of Pennsylvania
Building Rigid Networks with Prestress and Selective Pruning
John Crocker and Andrea Liu, University of Pennsylvania
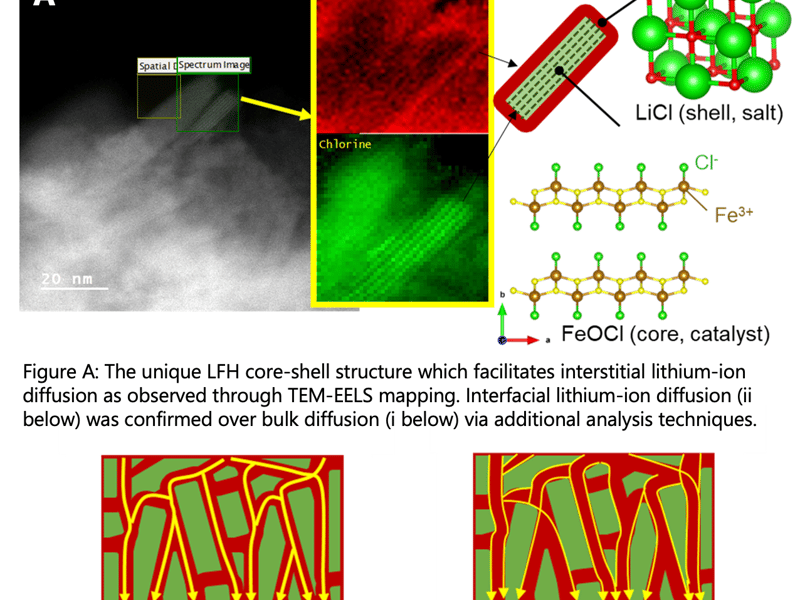
Fast Ionic Conduction Achieved Through Ceramic Heterointerface Design
User of Scientific Experimental Facilities: Toyota Research Institute of North America
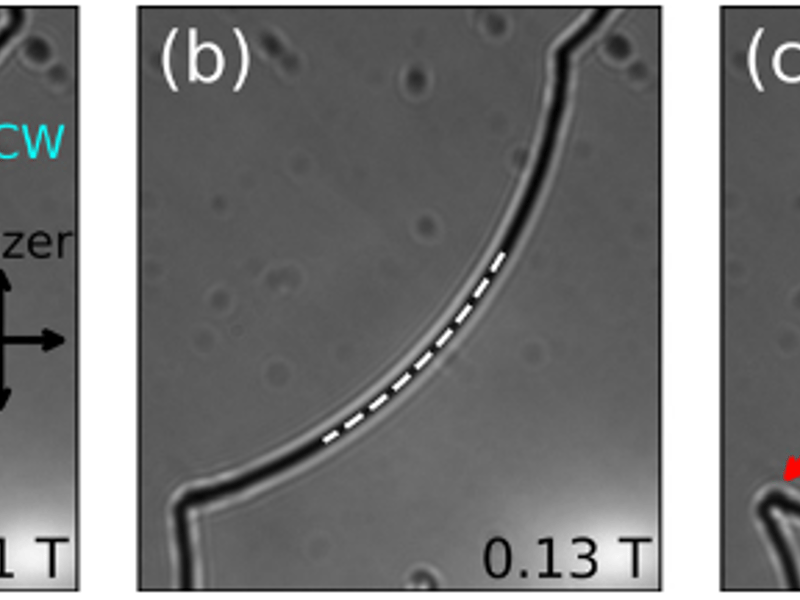
Measuring the Line Tension of Liquid Crystal Defects
Arjun Yodh, Jay Kikkawa, University of Pennsylvania; Peter Collings, Swarthmore
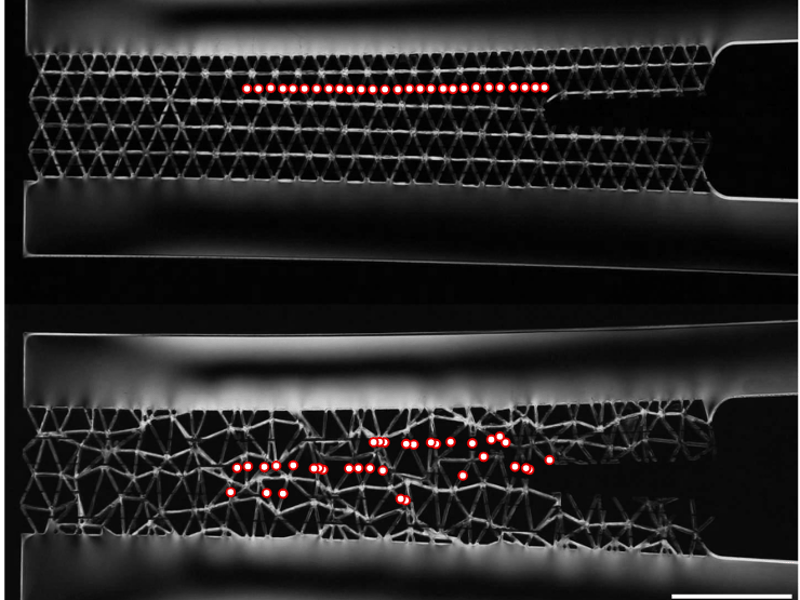
Enhancing Fracture Toughness in Mechanical Metamaterials through Disorder
Kevin T. Turner and Doug Durian, U. Pennsylvania & Michal Budzik, Aarhus U.
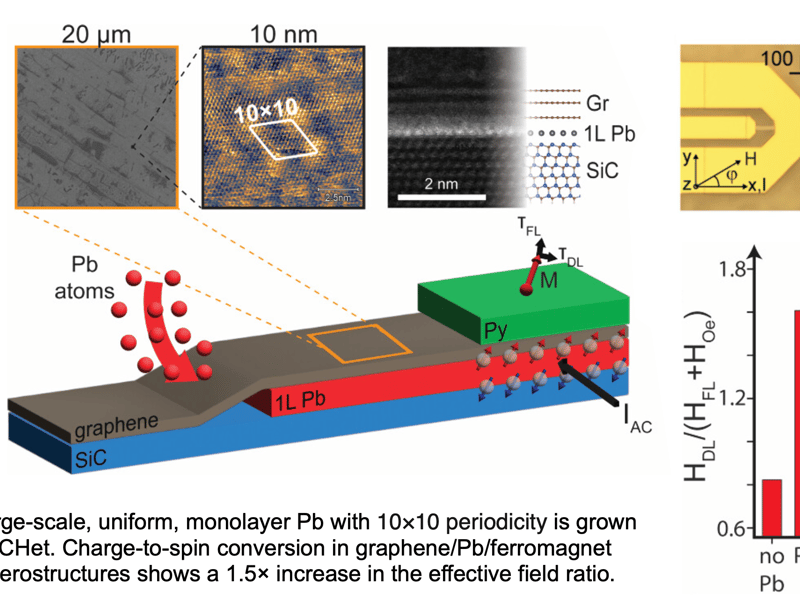
Large-Area Intercalated Two-Dimensional Pb/Graphene Heterostructure as a Platform for Generating Spin–Orbit Torque
Eli Rotenberg (LBNL), Nabil Bassim (MU), Adam Friedman (UM), Robert Wallac (UT Dallas), Chaoxing Liu, Nitin Samarth, Vincent Crespi, and Joshua Robinson