Rapid computational prediction of crystalline polymorphism
-
 The ability of an
The ability of an
organic molecular solid to crystallize into different structures is a phenomenon known as polymorphism.
- Polymorphism is an
issue of major concern in the pharmaceutical industry. In many drug compounds, some fraction
of the crystal structures that can be formed cause the drug to lose its
therapeutic function. If these
structures are not known at the time of the drug’s release onto the market,
they can turn up unexpectedly in the manufacturing process with potentially
serious consequences.
- We have developed a computational technique capable of
rapidly identifying these different crystalline forms. The method supplements
molecular dynamics with an algorithm for smoothly evolving the parameters of
the crystalline unit cell (right figure), thereby driving the molecules in the
unit cell from one crystal structure to another in a calculation that can be
performed in just a few hours on a standard desktop computer. The method also allows the crystal structures
to be ranked according in terms of their thermodynamic stability under a chosen
set of external conditions (see figure 2).
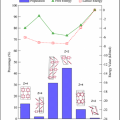 figure 2
figure 2
 The ability of an
The ability of an figure 2
figure 2