The National Society of Black Physicists recently held their Annual Conference, the largest academic meeting of minority physicists in the US in Knoxville, Tennessee.

The National Society of Black Physicists recently held their Annual Conference, the largest academic meeting of minority physicists in the US in Knoxville, Tennessee.

An outreach event led by CHARM postdocs and grad students drew almost 200 attendees in partnership with a local library. Students aged preK-8 participated in seven hands-on demonstration booths, including several booths that focused on materials science principles.
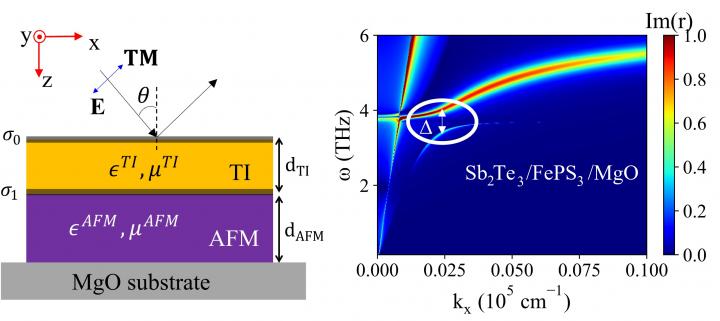
This research effort, carried out by the University of Delaware's MRSEC, provides a potential hybrid material platform for optoelectronic device applications in the THz frequency domain.
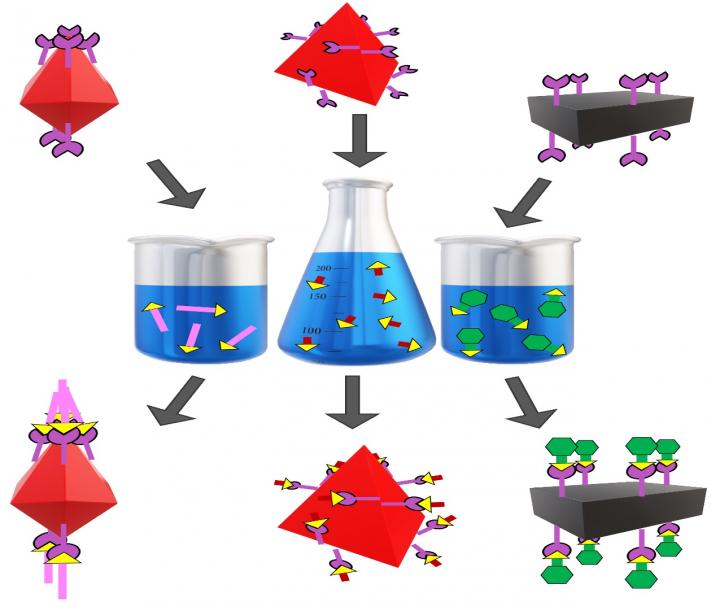
The University of Delaware MRSEC has shown, for the first time, that click chemistry can be used to functionalize multiple families of porous cages.

The LRSM spearheaded the inaugural Diversity Equity Engagement at Penn in STEM (DEEPenn STEM) weekend in October 2022. The initiative aims to proactively educate and recruit students from ethnically and racially minoritized communities (i.e. URMs), women, and first-generation low-income (FGLI) students to STEM-related graduate programs at Penn.

Philadelphia Materials Day is a collaborative effort between the University of Pennsylvania MRSEC and the Materials Science & Engineering Department at Drexel University to promote materials research in the region. The 12th annual Philadelphia Materials Day took place on February 11, 2023 at the Bossone Research Center at Drexel University.
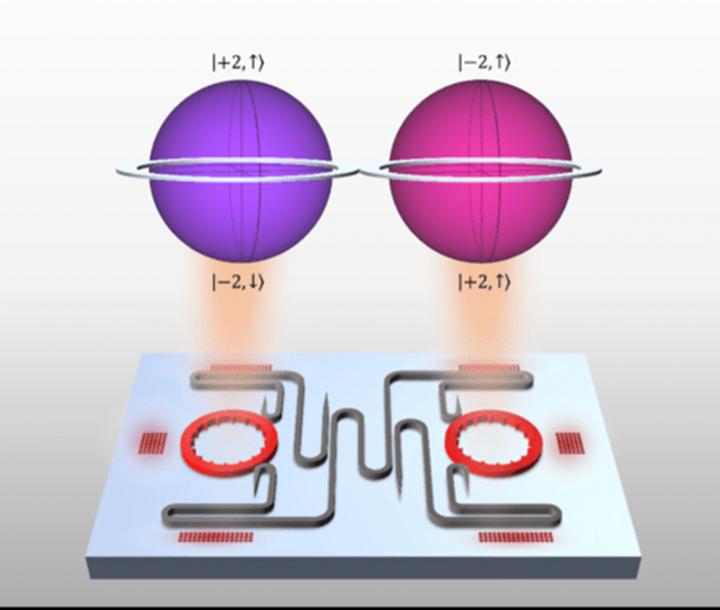
Researchers at the University of Pennsylvania have made a microfabricated laser using semiconductor fabrication methods that can control two features of the light particles: their orbit and their spin. This allows them to make light particles with four states simultaneously. These higher-dimensional quantum bits (qudits) can store more information and better avoid noise. They can also make quantum communication more secure and faster and allow more secure communications.

In conventional machine learning, a computer is used to minimize a cost function that specifies a desired task, using global information about the entire network. We have now demonstrated how machine learning tasks can be learned and performed without either a computer or global information by taking advantage of physics via a scheme called coupled learning1.
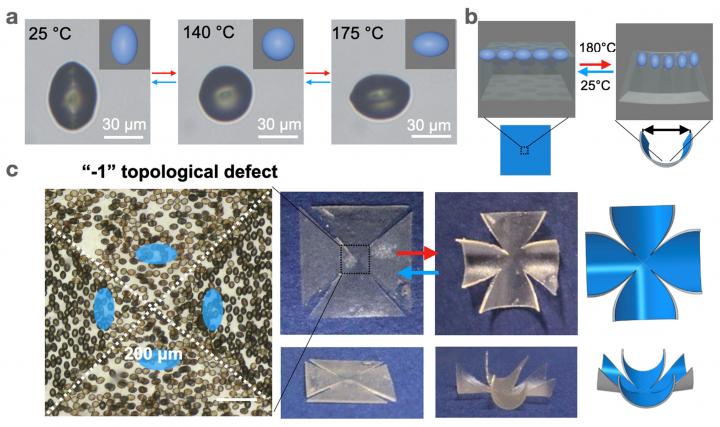
Liquid crystal elastomers (LCEs) with intrinsic molecular anisotropy can be preprogrammed to morph shapes from 2D to 3D under external stimuli. However, it is difficult to program the positions and orientations of individual building blocks separately and locally as they are chemically linked in the polymer network.
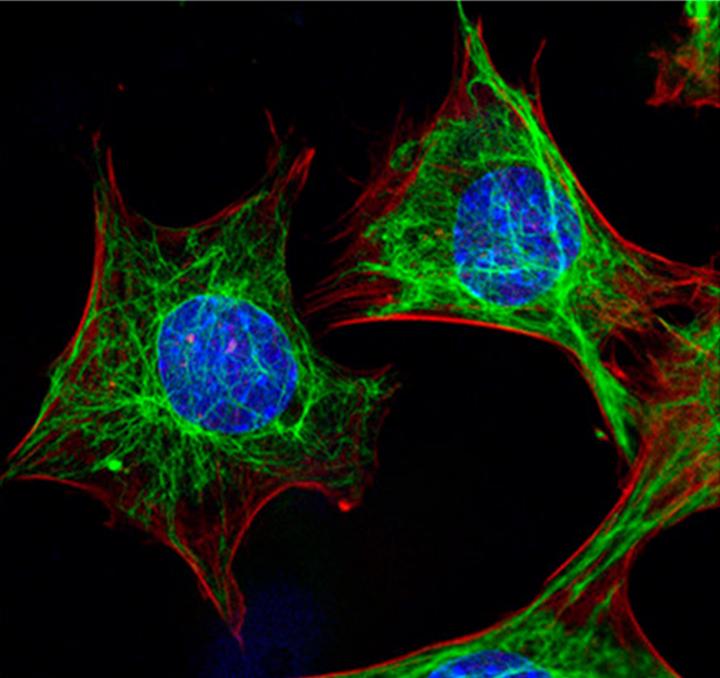
Cells and tissues are subjected to external mechanical stresses in the body, including compressive loads, pressure gradients, and shear. This study shows that single cells become harder when compressed and that the parts inside the cells that make them strong (called the cytoskeleton) change when they are compressed. Some cells, like fibroblasts, become harder when subjected to moderate compression. However, this does not happen if a part of the cytoskeleton called vimentin is removed. This is because vimentin networks become harder when compressed or extended. This is explained using a theoretical model to based on the flexibility of vimentin filaments and their surface charge, which resists volume changes of the network under compression.