Highlights
Feb 28, 2013
UPENN Materials Research Science and Engineering Centers
Topological Semimetal in Tensile Strained HgTe
C.L. Kane, E.J. Mele and A.M. Rappe, University of Pennsylvania
In the past few years, the theory of
topological band structures has been generalized beyond topological insulators
to include topological semimetals, including Weyl
semimetals, Dirac semimetals and other “symmetry protected” topological
states. HgTe is a
semimetal in which the degeneracy of the conduction and valence band at the G point is
protected by symmetry. In their early
work on topological insulators, Fu and Kane showed that straining HgTe opens a
gap at G,
resulting in a topological insulator.
Feb 20, 2013
Northwestern Materials Research Science and Engineering Center
Thermal Stability of Amorphous Zn-In-Sn-O Films Diana
Diana E. Proffit1, Thomas Philippe1, Jonathan D. Emery1, Qing Ma2, D. Bruce Buchholz1, Peter W. Voorhees1, Michael J. Bedzyk1, Robert P.H. Chang1, Thomas O. Mason1
Diana E. Proffit1, Thomas Philippe1, Jonathan D. Emery1, Qing Ma2, D. Bruce Buchholz1, Peter W. Voorhees1, Michael J. Bedzyk1, Robert P.H. Chang1, Thomas O. Mason1
1Northwestern University Materials Research Science & Engineering Center2DND-CAT, Northwestern Synchrotron Research Center at Advanced Photon
Feb 20, 2013
Northwestern Materials Research Science and Engineering Center
A Range of Amorphous Structures
D.B. Buchholz, L. Zeng, M.J. Bedzyk and R.P.H. Chang
A range of amorphous structures for a single
chemical-composition material (Indium Oxide)
were observed; the structure dependent on
the growth conditions.
The carrier mobility and film (not carrier)
density of the films was dependent on growth
temperature.
Films grown at 0°C and below are amorphous
The film density decreased from 7.0 g/cm3
at 0°C to 5.4 g/cm3 at -100°C; the carrier
mobility decrease from ~57 cm2/V•s to ~20
cm2/V•s over this same temperature range.
The peak in mobility at 0°C adds to the body
Feb 20, 2013
Northwestern Materials Research Science and Engineering Center
High Performance Carbon Nanotube Thin-Film Transistors Enabled by Hybrid Molecular Dielectrics
Vinod K. Sangwan, Rocio Ponce Ortiz, Justice M. P. Alaboson, Jonathan D. Emery, Michael J. Bedzyk, Lincoln J. Lauhon, Tobin J. Marks, and Mark C. Hersam
Over the past decade, semiconducting carbon
nanotube (CNT) thin films have been recognized as
contending materials for a wide range of applications
in electronics, energy, and sensing. Nevertheless,
CNT transistor performance suitable for real-world
applications awaits understanding-based progress in
the integration of independently pioneered device
components. We achieve this here by integrating
high-purity semiconducting CNT films with a customdesigned
hybrid inorganic-organic gate dielectric.
Jan 30, 2013
Triangle Small Angle X-Ray Scattering Facility
In an
effort, spearheaded by Triangle MRSEC, we received support through the NSF-MRI program
for the purchase of Small Angle X-Ray Scattering (SAXS) instrumentation.
The state-of-the-art instruments will serve the greater Research Triangle
community for
research and education, and will be housed in Duke's Shared Materials
Instrumentation Facility (SMIF).
Jan 19, 2013
Northwestern Materials Research Science and Engineering Center
X-ray Standing Wave Mapping of Graphene/SiC
J. Emery1, B. Detlefs2, H. Karmel1, V. Wheeler3, D.K. Gaskill3, M. Hersam1, J. Zegenhagen2, M. Bedzyk1
1Northwestern University Materials Research Science & Engineering Center
2European Synchrotron Radiation Facility, 3U.S. Naval Research Lab
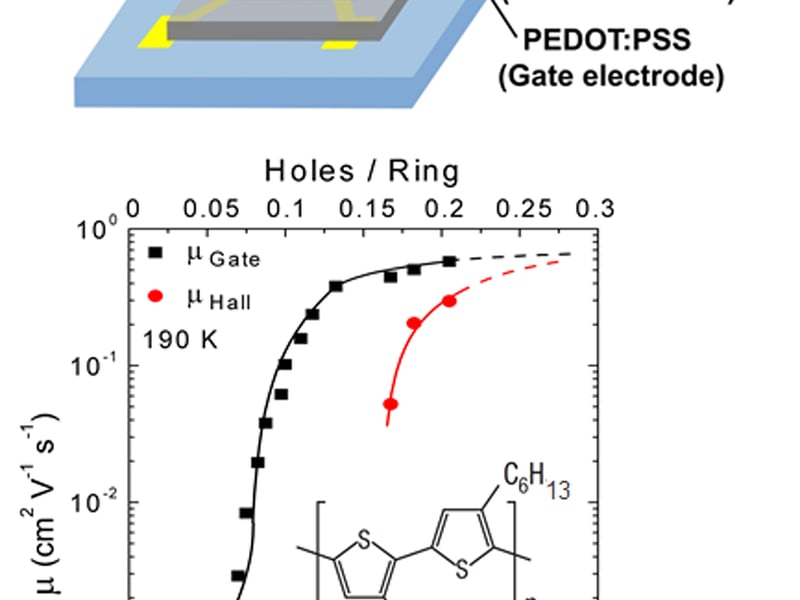
Jan 17, 2013
UMN Materials Research Science and Engineering Center (2014)
First Observation of Hall Effect in Polymer Transistors
C. Daniel Frisbie (IRG-2) & Chris Leighton (IRG-3)
Printed transistors employing both the bench-mark polymer semiconductor poly(3-hexyl-thiophene) and ultra-high capacitance ion gel gate insulators exhibit unusually large hole mobilities near 1 cm2/Vs at high charge densities (0.2 holes/ring).
Jan 16, 2013
Genetically Engineered Materials Science and Engineering Center (2005)
SAPs: Self Assembled Peptides
Developed in GEMSEC, biocombinatorially selected solid binding peptides with short (7-15) amino acid (AA) sequences can bind to atomically flat materials via molecular recognition that leads to surface diffusion, clustering and long-range ordered assembly commensurate with the underlying crystallographic solid lattice.
Showing 831 to 840 of 1394