Highlights

Jun 5, 2018
Northwestern Materials Research Science and Engineering Center
HerStory at the Chicago Museum of Science and Industry
In collaboration with the Chicago Museum of Science and Industry, HerStory is an outreach event that encourages young girls, particularly underrepresented minorities, to pursue science in academia and beyond. The event agenda includes a massive scavenger hunt at the museum that featured exhibits of famous female scientists in each wing of the museum. Volunteers and young women from across the Chicagoland area participated in the event.
Jun 5, 2018
Northwestern Materials Research Science and Engineering Center
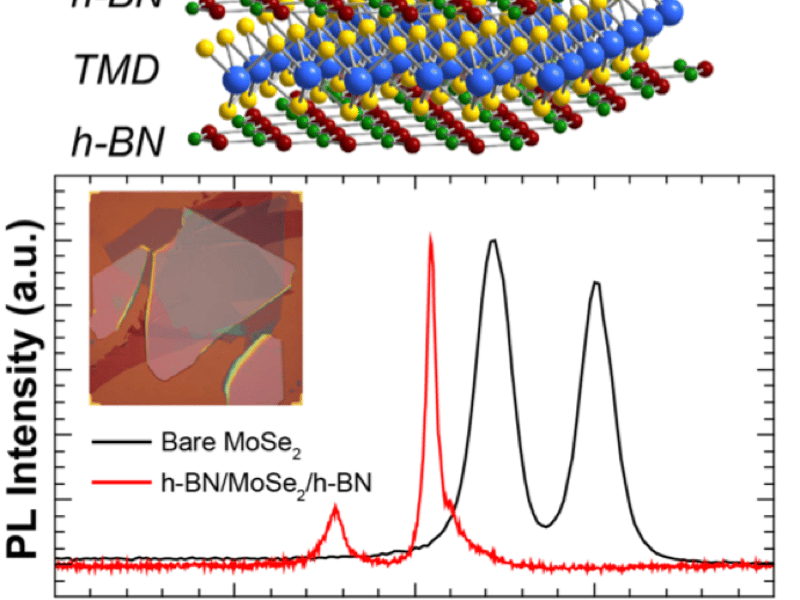
Encapsulated 2D Heterostructures for Enhanced Layered Optoelectronics
Two-dimensional (2D) layered materials have many features suitable for optoelectronic devices, but poor quality substrates can degrade optical properties. By encapsulating a monolayer semiconductor in layers of atomically-thin hexagonal boron nitride, a nearly pristine environment can be achieved free from surface roughness and defects of typical substrates.
Jun 5, 2018
Northwestern Materials Research Science and Engineering Center
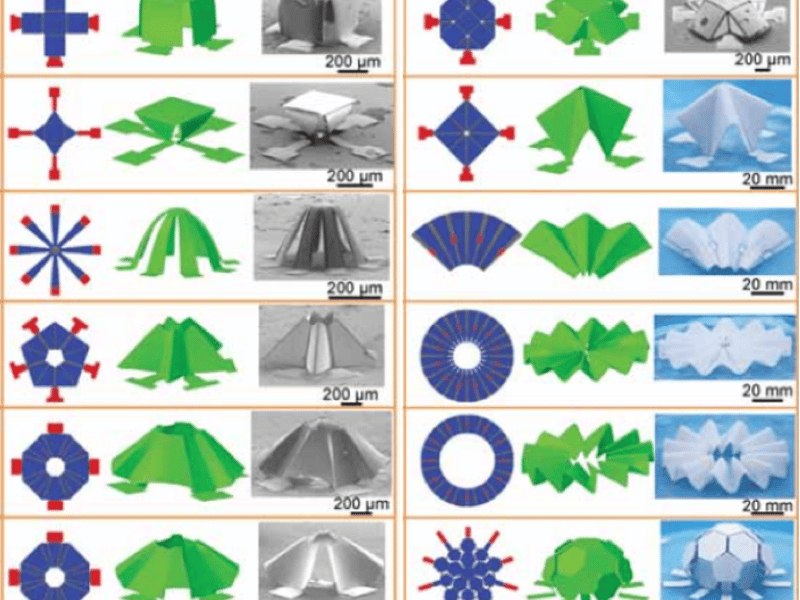
Controlled Mechanical Buckling for Origami-Inspired 3D Microstructures
A new strategy has been introduced to exploit mechanical buckling for autonomic origami assembly of three-dimensional (3D) microstructures across a wide range of material classes, including soft polymers and brittle inorganic semiconductors, and length scales from nanometers to centimeters. The engineered folding creases are created through spatial variation of thickness in the initial two-dimensional structures.
Jun 5, 2018
Northwestern Materials Research Science and Engineering Center
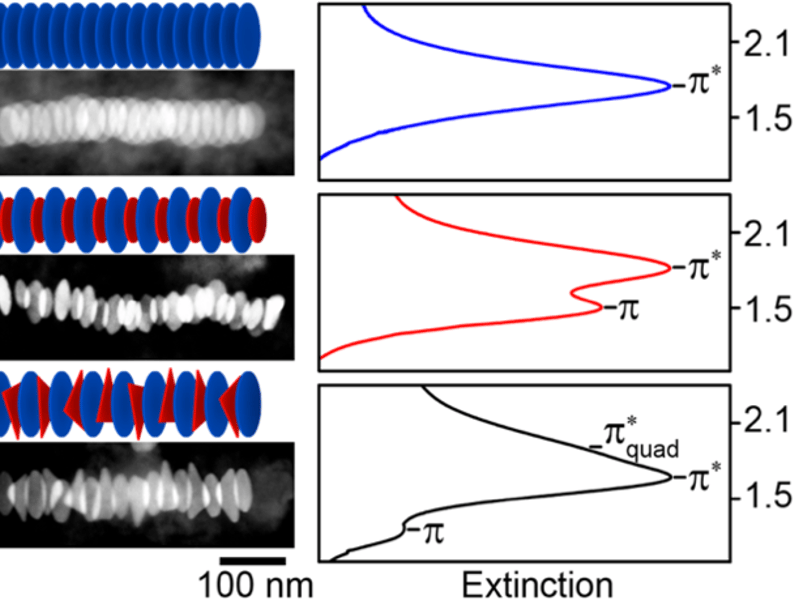
Tuning Optical Properties with DNA-Linked Gold Nanodisk Stacks
Recent advances in gold nanoparticle synthesis combined with functionalization with DNA linkers has enabled the self-assembly of stacks of gold nanodisks in which the optical spectra can be tuned and modulated by controlling the stack structure (e.g., particle spacing, arrangement, and stack length). The figure shows three possible arrangements of the particles, and the corresponding spectra that are associated with the plasmon resonance excitation in the stack.
Jun 5, 2018
Northwestern Materials Research Science and Engineering Center
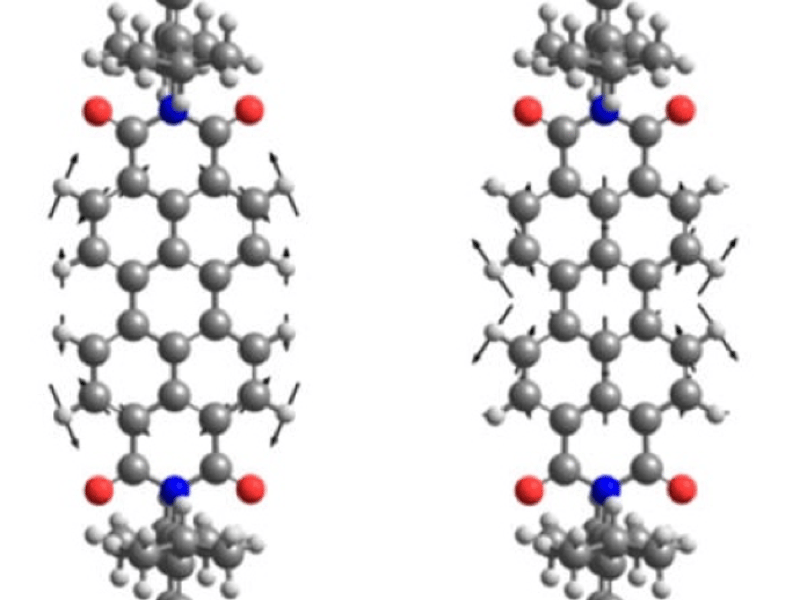
Probing Intermolecular Interactions with Intramolecular Resolution
At the nanometer-scale, the surface area to volume ratio increases substantially compared to bulk materials. Consequently, methods for functionalizing and passivating surfaces can play a dominant role in determining the properties of nanomaterials. Of particular interest are self-assembled monolayers of organic molecules that have been widely used to control the electronic, optical, chemical, and frictional properties of nanomaterials in a range of applications.
Jun 5, 2018
Northwestern Materials Research Science and Engineering Center
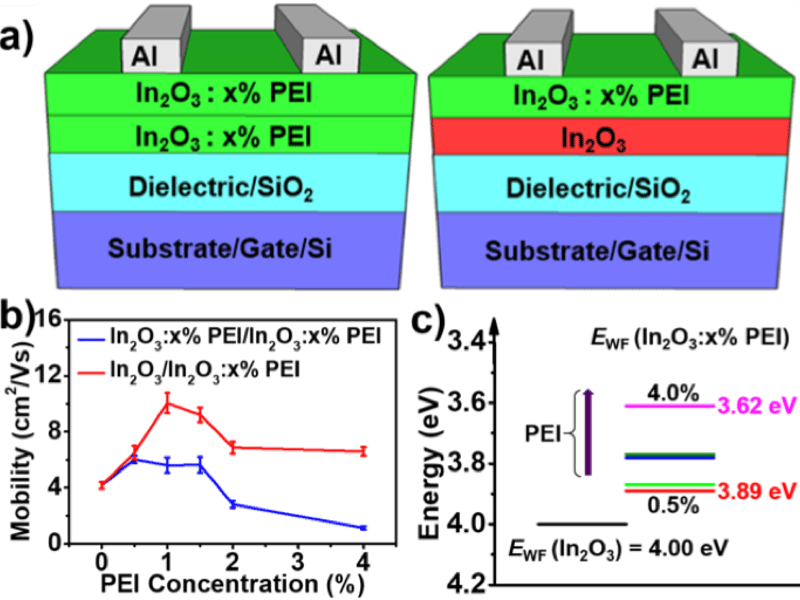
High Performance Heterojunction Oxide Thin Film Transistors
Due to their outstanding electronic properties and high optical transparency, metal oxide thin-film transistors have significant potential in state-of-the-art flat panel display technologies. Here, high performance solution-processed metal oxide thin-film transistors were realized by fabricating heterojunctions of indium oxide (In2O3) and polyethylenimine (PEI) as the semiconducting channel layer. Due to the tunable work function of the In2O3-PEI blends, electron mobilities as high as ~10 cm2V-1s-1 were obtained.
Jun 5, 2018
Northwestern Materials Research Science and Engineering Center
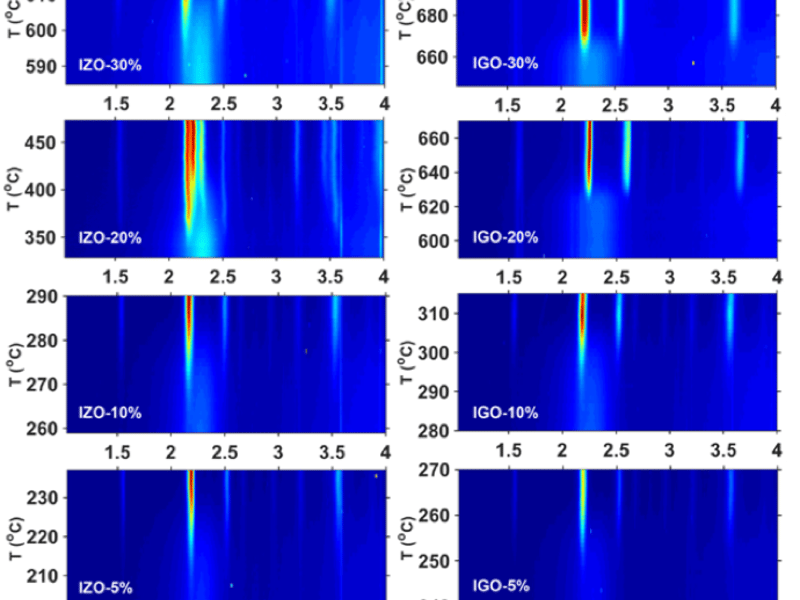
Amorphous to Crystalline Transition in Indium Oxide Semiconductors
Amorphous oxide semiconductors commonly are indium oxides doped with other metal ions. Although it is known that the introduction of secondary metal ions decreases the degree of crystallinity and elevates the crystallization temperature, there is a lack of systematic study to compare and quantify the effects of different dopant elements. In an interdisciplinary study within IRG-2 of the Northwestern University MRSEC, in situ synchrotron X-ray characterization was performed to characterize the isochronal crystallization process of oxide thin films synthesized by pulsed laser deposition.
Jun 5, 2018
Northwestern Materials Research Science and Engineering Center
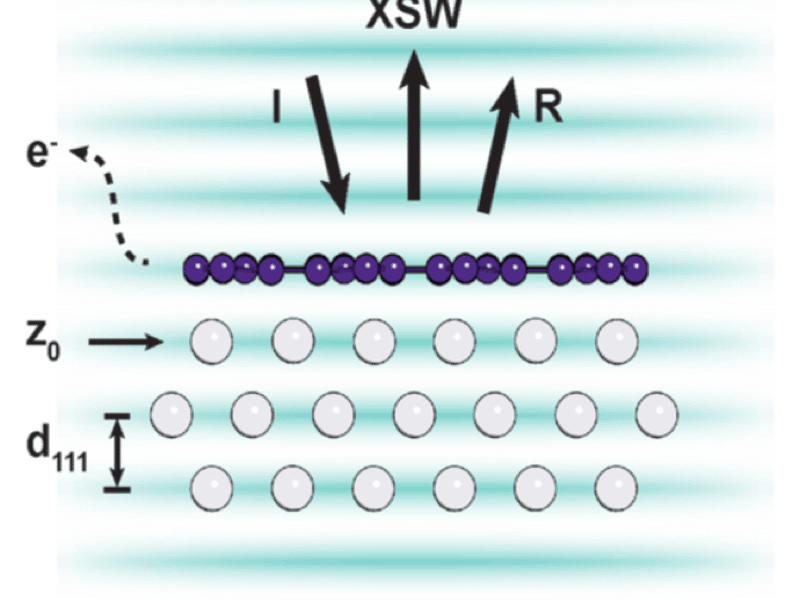
Atomic-Scale Characterization of Synthetic Two-Dimensional Materials
Atomically thin two-dimensional (2D) materials exhibit superlative properties dictated by their intralayer atomic structure, which is typically derived from a limited number of thermodynamically stable bulk layered crystals (e.g., graphene from graphite). The growth of entirely synthetic 2D crystals – those with no corresponding bulk allotrope – would circumvent this dependence upon bulk thermodynamics and substantially expand the phase space available for structure-property engineering of 2D materials.
Jun 5, 2018
Northwestern Materials Research Science and Engineering Center
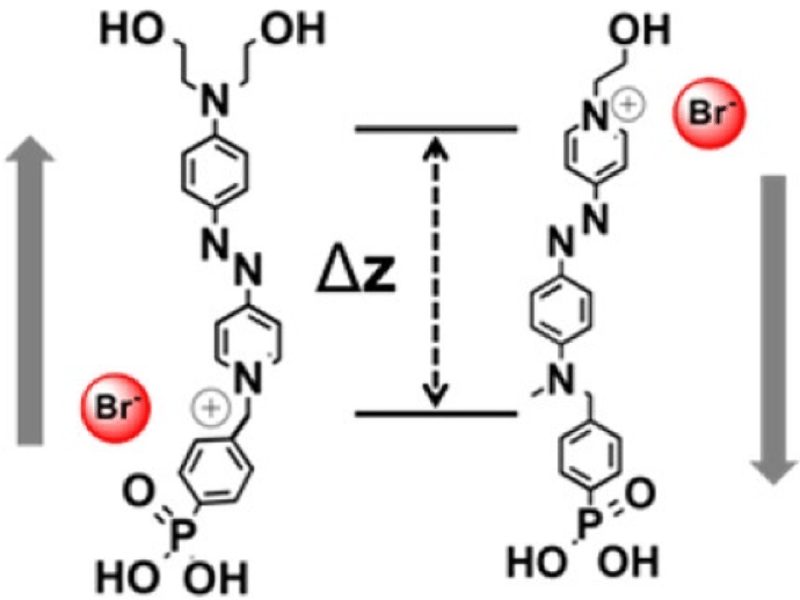
Controlling Dielectric Polarization via Molecular Design
Dielectric materials play a critical role in determining the operating voltage in modern-day electronics. In particular, highly polarizable and ultrathin dielectrics enable low operating voltages and thus low power consumption.
Jun 5, 2018
Cornell Center for Materials Research (2017)
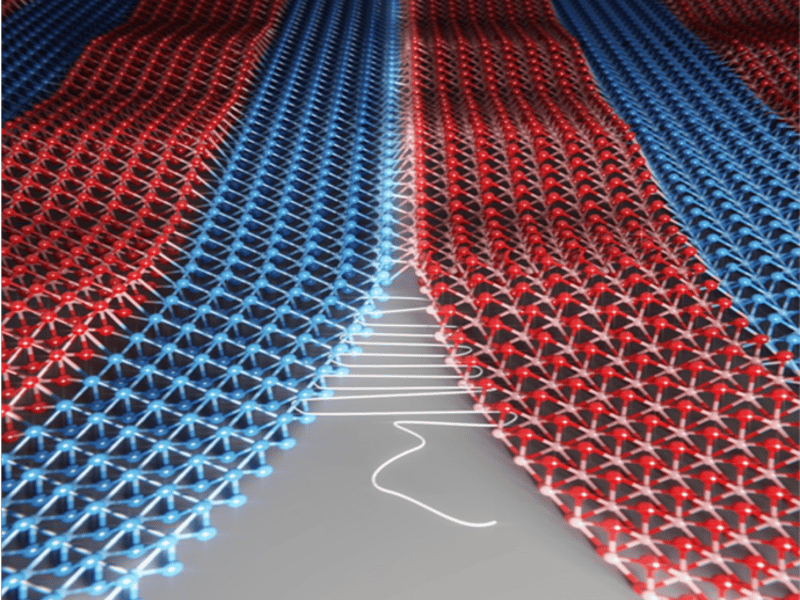
Three-Atom Thick Fabrics Made by Seamless Stitching of Single-Layer Crystals
Joining different materials can lead to all kinds of breakthroughs. In electronics, this produces heterojunctions — the most fundamental components in solar cells and computer chips. The smoother the seam between two materials, the better the electronic devices will function.
Showing 381 to 390 of 1394