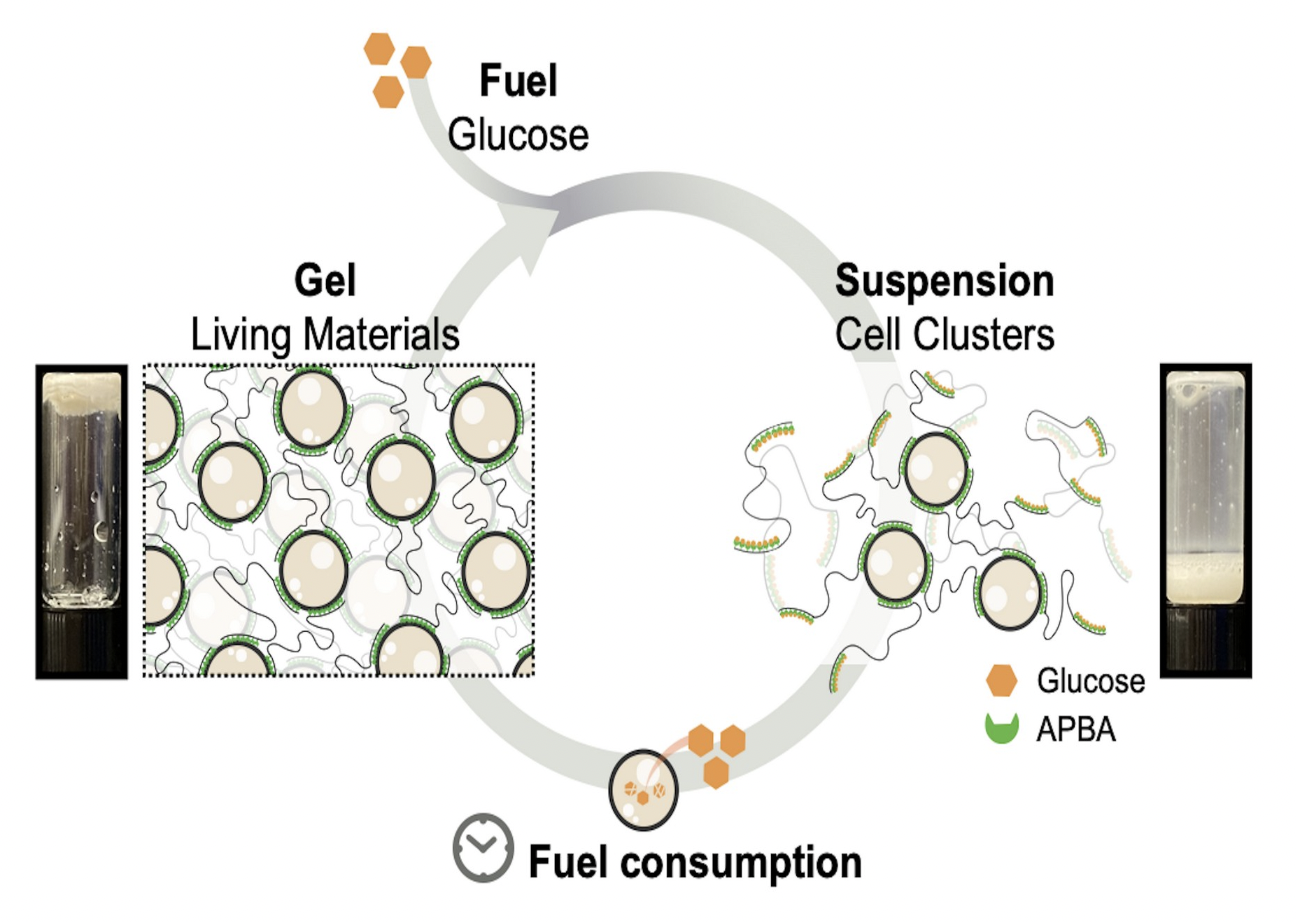
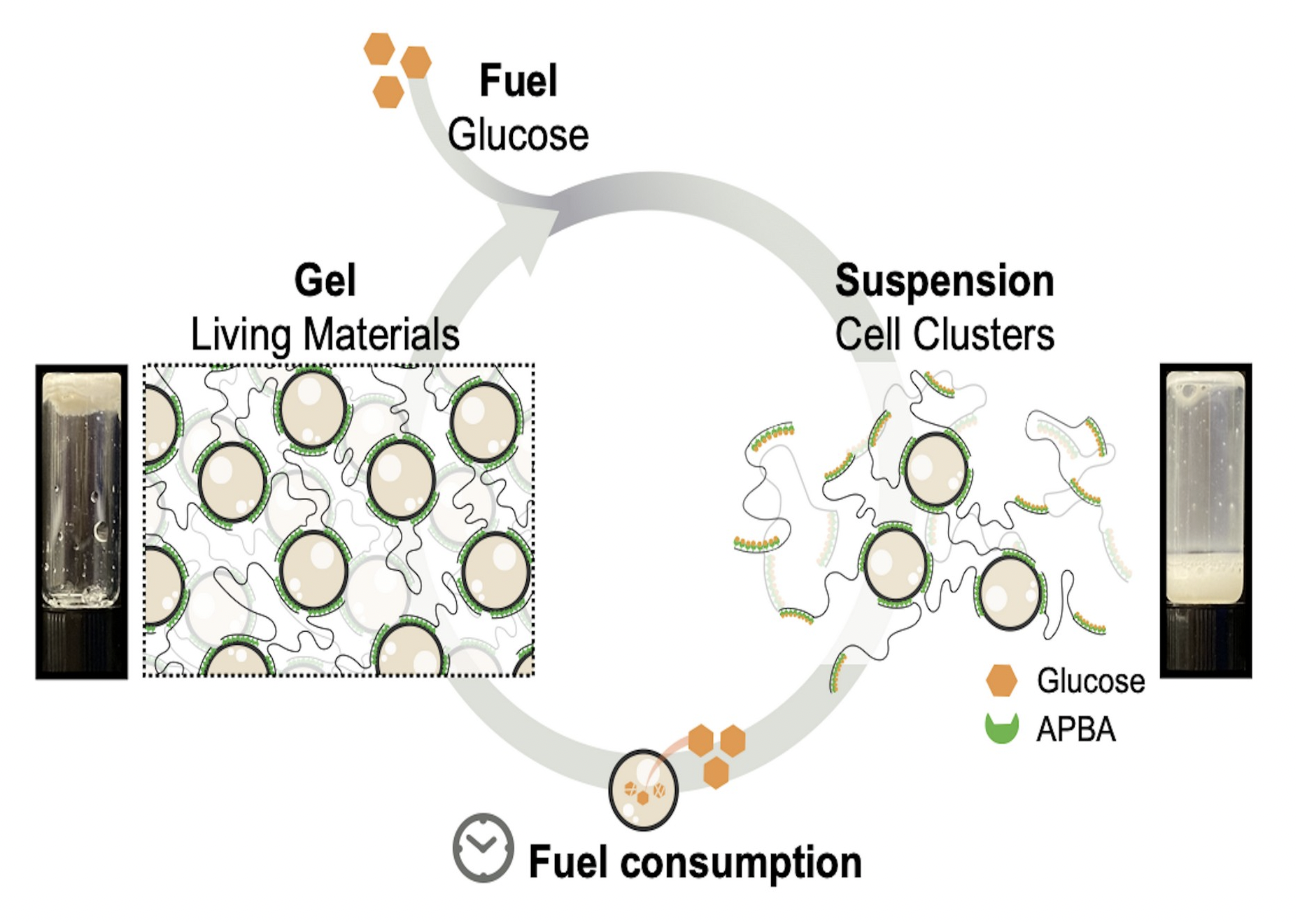
- The first example of synthetic living material featuring dissipative behaviors directly controlled by the fuel consumption of their constituent cells
- A synthetic dissipative system that interfaces biology and shows repeated macroscopic phase transition
- Detailed examination of kinetics of fuel consumption by living cells at a molecular level
Impact:
- This work significantly expands the scope of dissipative materials by bringing it one step closer to integration with biology.
- This work provides a new tool and knowledge to design synthetic dissipative systems with living cells.

Center for Complex and Active Materials
The primary mission of he MRSEC at UCI is to establish foundational knowledge in materials science and engineering of new classes of materials offering unique and broad functionality via an interplay among design, simulation, synthesis, and advanced characterization.