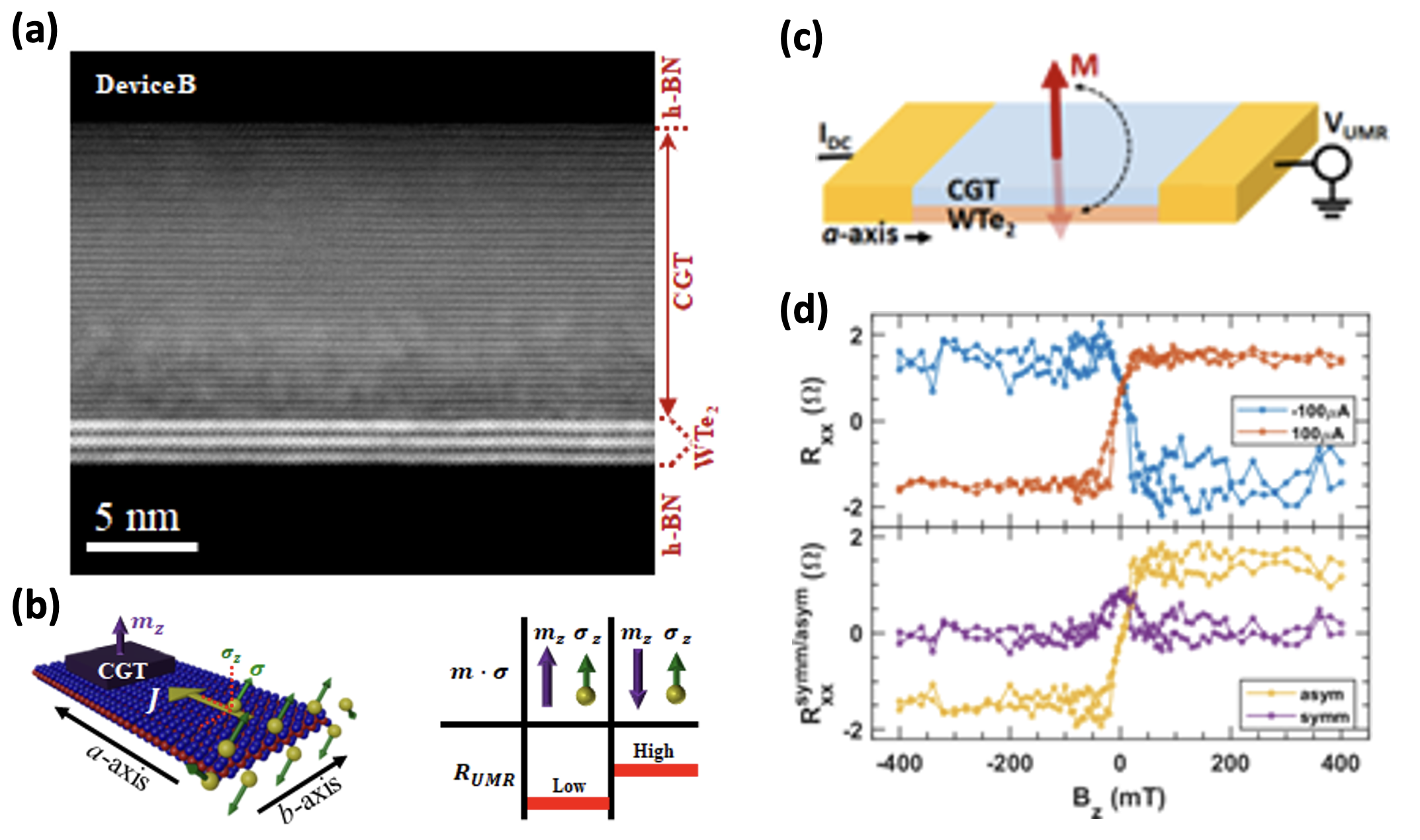
Unconventional unidirectional magnetoresistance in heterostructures of a topological semimetal and a ferromagnet
Currently, spin-orbit torque based two-terminal magnetic memory device, like commercially available magnetic-tunnel-junction-based magnetic memory devices, is missing due to the lack of identified magnetoresistance phenomena to distinguish the up and down states of a perpendicular polarized magnet in bilayer heterostructure.
Unidirectional magnetoresistance (UMR) is a change in the longitudinal resistance of a heterostructure, composed of a spin-source material and a magnetic layer, due to magnetization reversal and its interaction with non-equilibrium spin accumulation.
Atomically clean bilayer heterostructures consisting of a low-symmetry semimetal (WTe2) and a ferromagnetic semiconductor (Cr2Ge2Te6, CGT) was employed.
Unconventional UMR originates from the interplay of crystal symmetry-breaking in WTe2 and magnetic exchange interaction across the WTe2/CGT interface.
This work was published in Kao et al., Nature Materials in March 2025.
Unconventional unidirectional magnetoresistance in heterostructures of a topological semimetal and a ferromagnet

Center for Emergent Materials
The Center for Emergent Materials (CEM) performs innovative multidisciplinary science focused on discovery and engineering of emergent materials to enable novel phenomena and phases.